Unveiling the Advantages of Flexible Spending Accounts: A Comprehensive Guide to FSA Products
Related Articles: Unveiling the Advantages of Flexible Spending Accounts: A Comprehensive Guide to FSA Products
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Advantages of Flexible Spending Accounts: A Comprehensive Guide to FSA Products. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Advantages of Flexible Spending Accounts: A Comprehensive Guide to FSA Products
_Work.png?width=1920u0026height=1080u0026name=How_Does_a_Flexible_Spending_Account_(FSA)_Work.png)
Flexible spending accounts (FSAs) are powerful financial tools that allow individuals to set aside pre-tax dollars for specific eligible expenses, offering significant tax savings. These accounts, often offered through employers, empower employees to manage healthcare and dependent care costs effectively.
Understanding the Core Principles of FSAs:
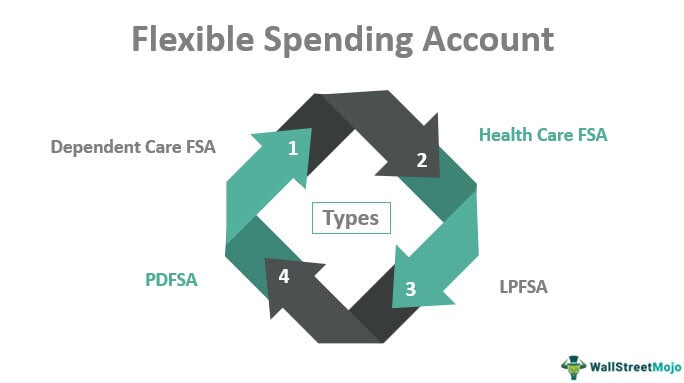
FSAs function on the principle of "use it or lose it," meaning any unused funds at the end of the plan year are forfeited. This characteristic, though seemingly restrictive, incentivizes responsible spending and planning. There are two primary types of FSAs:
- Healthcare Flexible Spending Accounts (HFSA): These accounts are designed to cover out-of-pocket healthcare expenses not covered by insurance, such as deductibles, copayments, and prescription drugs.
- Dependent Care Flexible Spending Accounts (DCFSA): These accounts cater to expenses related to the care of dependents, such as childcare, elder care, or adult daycare.
The Benefits of Utilizing FSAs:
FSAs provide a multitude of advantages for individuals, including:
- Tax Savings: By contributing to an FSA, individuals can reduce their taxable income, leading to potential tax savings. The amount saved depends on the individual’s tax bracket.
- Increased Affordability: FSAs make it easier to manage healthcare and dependent care costs by providing a dedicated source of funds for these expenses. This can be particularly beneficial for families with young children or aging parents.
- Greater Control over Finances: Individuals have greater control over their healthcare and dependent care spending by using pre-tax dollars. This allows for more strategic budgeting and financial planning.
- Potential for Reduced Health Insurance Premiums: In some cases, employers may offer lower health insurance premiums to employees who participate in FSAs, further enhancing the cost-effectiveness of these accounts.
- Convenience and Flexibility: FSAs offer a convenient way to manage healthcare and dependent care expenses, allowing individuals to access funds quickly and easily.
Eligibility Criteria and Participation:
Eligibility for FSAs is typically determined by an employer’s plan. Generally, employees who work for an employer offering an FSA program are eligible to participate. However, specific eligibility criteria may vary depending on the employer’s plan.
Contribution Limits and Maximums:
The IRS sets annual contribution limits for FSAs. These limits are subject to change annually and are typically adjusted for inflation. For 2023, the annual contribution limit for both HFSA and DCFSA is $2,850 per person.
Key Considerations for FSA Utilization:
- Estimate Healthcare and Dependent Care Expenses: It is crucial to carefully estimate healthcare and dependent care expenses for the year to determine the appropriate contribution amount to an FSA. Overestimating can lead to forfeited funds, while underestimating may result in insufficient funds to cover expenses.
- Plan for Potential Changes in Expenses: Life circumstances can change unexpectedly, impacting healthcare and dependent care needs. It is essential to consider potential changes in expenses when determining contribution amounts.
- Understand the "Use It or Lose It" Rule: Remember that unused funds in an FSA are forfeited at the end of the plan year. It is essential to plan spending to maximize utilization of FSA funds.
- Review FSA Options and Eligibility: Carefully review the FSA plan offered by your employer, including contribution limits, eligible expenses, and any applicable restrictions.
- Utilize FSA Funds Strategically: Plan your healthcare and dependent care expenses to make the most of FSA funds. For example, consider scheduling elective procedures or filling prescriptions early in the plan year to maximize utilization.
FAQs: Demystifying FSA Products
Q: What are some examples of eligible expenses for an HFSA?
A: Eligible expenses for an HFSA include:
- Deductibles and Copayments: Payments made towards deductibles and copayments for healthcare services.
- Prescription Drugs: Costs associated with prescription medications, including copayments and coinsurance.
- Vision Care: Expenses related to eye exams, eyeglasses, and contact lenses.
- Dental Care: Costs associated with dental checkups, cleanings, fillings, and other dental procedures.
- Over-the-Counter (OTC) Medications: Certain OTC medications, such as pain relievers, allergy medications, and first aid supplies, are eligible for reimbursement.
- Medical Equipment: Costs associated with medical equipment, such as crutches, walkers, and wheelchairs.
Q: What are some examples of eligible expenses for a DCFSA?
A: Eligible expenses for a DCFSA include:
- Childcare: Costs associated with daycare, preschool, and after-school programs for children under the age of 13.
- Eldercare: Expenses related to care for elderly dependents, including adult daycare, home healthcare, and assisted living facilities.
- Other Dependent Care: Costs associated with care for dependents with disabilities, regardless of age.
Q: How do I contribute to an FSA?
A: Contributions to FSAs are typically made through payroll deductions. Your employer will deduct a specific amount from your paycheck each pay period, which is deposited into your FSA account.
Q: What happens to unused funds at the end of the plan year?
A: Unused funds in an FSA are forfeited at the end of the plan year. This is known as the "use it or lose it" rule.
Q: Can I withdraw money from my FSA at any time?
A: Generally, you cannot withdraw money from an FSA at any time. Funds can only be used to pay for eligible expenses.
Q: What are some tips for maximizing FSA utilization?
A: Here are some tips for maximizing FSA utilization:
- Plan Ahead: Carefully estimate your healthcare and dependent care expenses for the year to determine the appropriate contribution amount.
- Schedule Elective Procedures Early: If you are planning an elective procedure, consider scheduling it early in the plan year to utilize FSA funds.
- Fill Prescriptions Early: Fill prescriptions early in the plan year to ensure that you have enough funds to cover any refills.
- Keep Track of Expenses: Keep detailed records of all eligible expenses to ensure accurate reimbursement.
- Utilize FSA Funds for OTC Medications: Consider using FSA funds for OTC medications that are eligible for reimbursement.
Conclusion: Empowering Financial Wellness through FSAs
FSAs play a vital role in empowering individuals to manage healthcare and dependent care expenses effectively. By offering tax savings, increased affordability, and greater control over finances, FSAs contribute significantly to overall financial well-being. Understanding the benefits, eligibility criteria, and utilization guidelines of FSAs can unlock substantial financial advantages for individuals and families.
.png?width=2880u0026height=1620u0026name=Pros_and_Cons_of_a_Flexible_Spending_Account_(FSA).png)
_-_FI.png#keepProtocol)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Advantages of Flexible Spending Accounts: A Comprehensive Guide to FSA Products. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
