Unraveling the Roots of Skin Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide to Risk Factors and Prevention
Related Articles: Unraveling the Roots of Skin Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide to Risk Factors and Prevention
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Roots of Skin Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide to Risk Factors and Prevention. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Roots of Skin Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide to Risk Factors and Prevention

Skin cancer, a prevalent and potentially life-threatening disease, arises from uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells within the skin. While various factors can contribute to its development, understanding the underlying causes is crucial for effective prevention and early detection. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate web of risk factors associated with skin cancer, shedding light on their impact and offering valuable insights into mitigating potential threats.
The Sun: A Major Culprit
The sun, while a vital source of vitamin D, also harbors a potent threat: ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Excessive exposure to UV rays, particularly from the sun’s harmful UVB and UVA wavelengths, damages DNA within skin cells, triggering mutations that can lead to cancerous growth. This damage accumulates over time, increasing the risk of skin cancer with prolonged sun exposure.
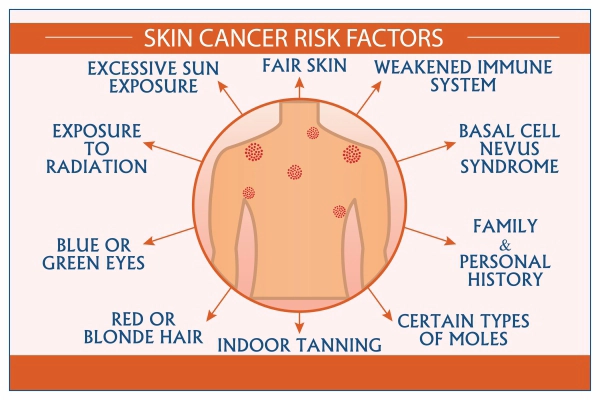
Skin Type and Genetics: Predisposition and Inheritance
Individual skin type plays a significant role in susceptibility to skin cancer. Fair skin, light hair, and blue eyes indicate a lower melanin content, making the skin more vulnerable to UV damage. Genetic predisposition also plays a crucial role. Family history of skin cancer significantly increases the risk, suggesting an inherited susceptibility to the disease.
Other Risk Factors: A Multifaceted Picture
Beyond sun exposure and genetics, numerous other factors contribute to the development of skin cancer. These include:
- Age: The risk of skin cancer increases with age, as cumulative sun damage takes its toll.
- Weakened Immune System: Conditions like HIV/AIDS or organ transplantation, which suppress the immune system, elevate the risk of skin cancer.
- Certain Medical Treatments: Radiation therapy and chemotherapy can damage skin cells and increase the risk of skin cancer.
- Exposure to Certain Chemicals: Some chemicals, like arsenic and coal tar, are known carcinogens and can contribute to skin cancer development.
- Lifestyle Habits: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor diet can weaken the immune system and increase susceptibility to skin cancer.
Types of Skin Cancer: Understanding the Spectrum
Skin cancer encompasses various types, each with distinct characteristics and treatment approaches. The three main categories are:
- Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC): The most common type, BCC typically appears as a pearly or waxy bump, often with a central depression. It usually grows slowly and rarely metastasizes.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC): Less common than BCC, SCC presents as a firm, red nodule or a flat, scaly lesion. It can grow more aggressively than BCC and has a higher risk of metastasis.
- Melanoma: The most dangerous type, melanoma originates from melanocytes, the cells responsible for pigmentation. It can appear in various forms, including moles, freckles, or even seemingly normal skin. Melanoma is highly aggressive and has a high risk of spreading to other organs.
Prevention: A Multifaceted Approach
While some risk factors are inherent, others can be mitigated through preventive measures. These include:
- Sun Protection: Limiting sun exposure during peak hours (10 am to 4 pm), wearing protective clothing (long sleeves, hats, sunglasses), and applying sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher are essential for safeguarding the skin from harmful UV rays.
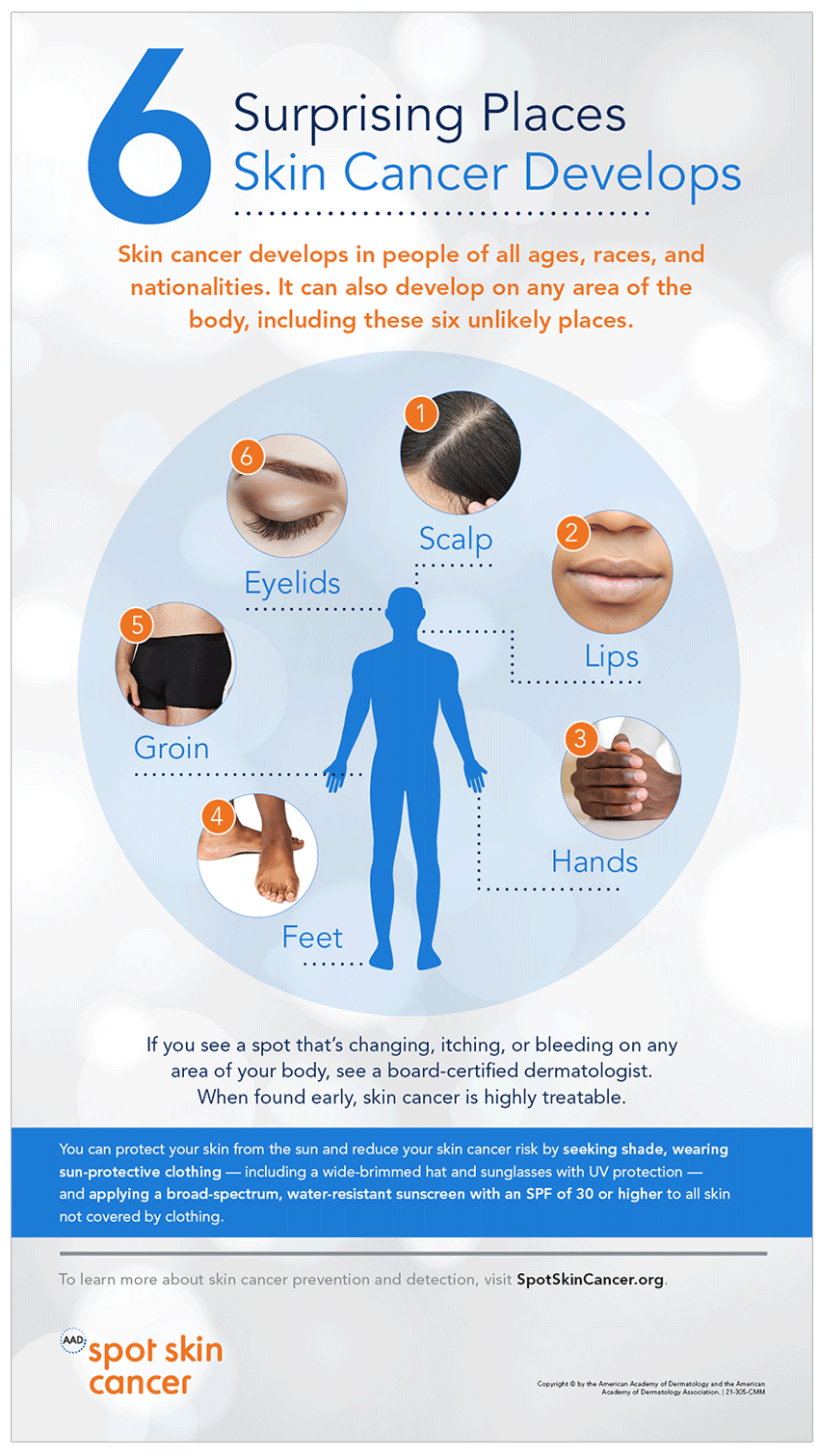
- Regular Skin Exams: Performing self-exams monthly and undergoing annual skin cancer screenings by a dermatologist are crucial for early detection and treatment.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, avoiding smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption contribute to overall health and immune function, potentially reducing skin cancer risk.
FAQs on Skin Cancer Risk Factors
Q: What are the most common types of skin cancer?
A: The most prevalent types are basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). Melanoma, while less common, is the most aggressive and dangerous type.
Q: Is skin cancer hereditary?
A: While not directly inherited, a family history of skin cancer increases the risk due to genetic predisposition.
Q: Can tanning beds cause skin cancer?
A: Yes, tanning beds emit UV radiation, posing the same risks as sun exposure and significantly increasing the risk of skin cancer.
Q: What should I do if I notice a suspicious mole?
A: Consult a dermatologist immediately. They can evaluate the mole and determine if further investigation or treatment is necessary.
Q: Can I prevent skin cancer completely?
A: While complete prevention is not always possible, adopting preventive measures like sun protection, regular skin exams, and healthy lifestyle choices can significantly reduce the risk.
Tips for Protecting Your Skin from Skin Cancer
- Seek shade: Limit sun exposure during peak hours, especially between 10 am and 4 pm.
- Cover up: Wear protective clothing, including long sleeves, pants, hats, and sunglasses.
- Apply sunscreen: Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, reapplying every two hours, especially after swimming or sweating.
- Check your skin: Perform monthly self-exams, paying attention to any changes in moles or other skin lesions.
- See a dermatologist: Schedule annual skin cancer screenings with a dermatologist, especially if you have a family history of skin cancer or have fair skin.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
Skin cancer is a serious health concern, but knowledge and preventive measures can significantly reduce its incidence and impact. By understanding the risk factors, adopting preventive strategies, and seeking early detection, individuals can empower themselves to safeguard their skin health. This comprehensive guide serves as a valuable resource, empowering readers to make informed decisions and proactively protect themselves from the dangers of skin cancer. Remember, early detection and timely treatment are crucial for successful outcomes, making awareness and vigilance paramount in the fight against this prevalent disease.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Roots of Skin Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide to Risk Factors and Prevention. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
