Unraveling the Causes of Skin Pain: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Unraveling the Causes of Skin Pain: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Causes of Skin Pain: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Causes of Skin Pain: A Comprehensive Guide

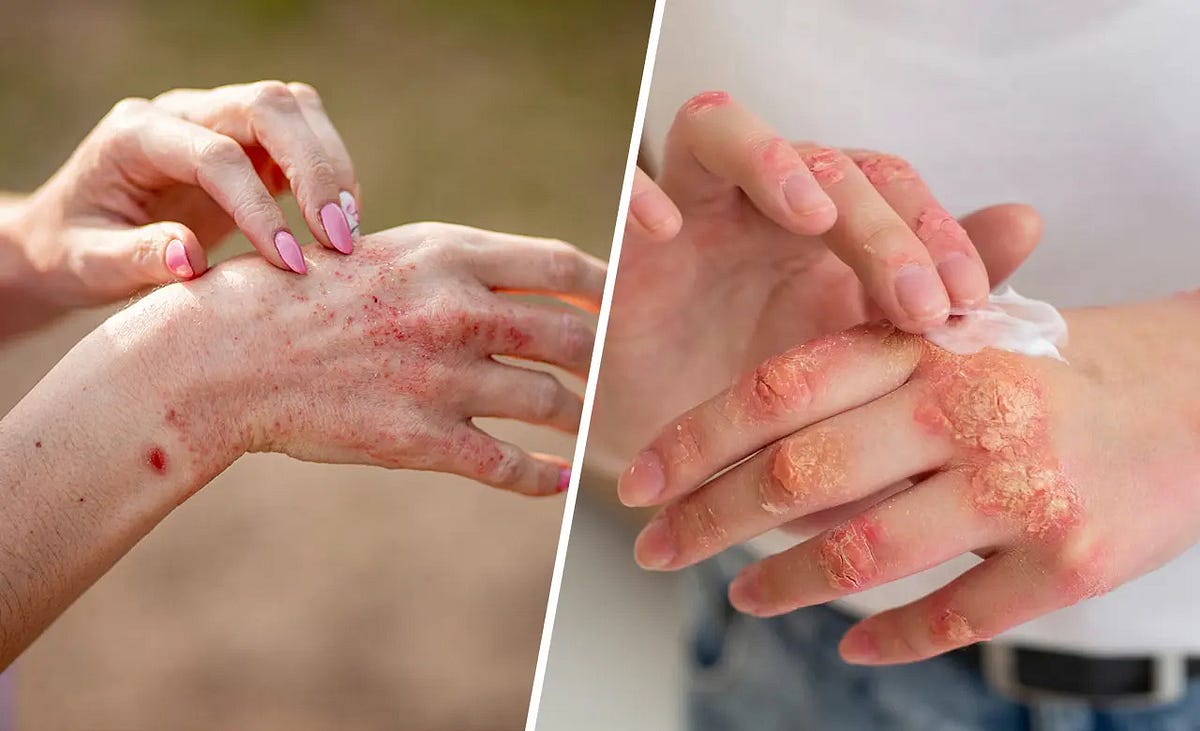
Skin pain, a sensation that can range from mild discomfort to excruciating agony, is a common experience. It can arise from a multitude of factors, each with its own unique underlying mechanism. Understanding these causes is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. This article delves into the diverse range of factors that can lead to skin pain, providing a comprehensive overview of its potential origins.
The Skin’s Complex Sensory System:
Before exploring the specific causes of skin pain, it is essential to understand the intricate sensory system of the skin. This system, composed of specialized nerve endings, detects various stimuli, including touch, temperature, pressure, and pain. When these nerve endings are activated, they transmit signals to the brain, which interprets them as sensations.
External Factors:
- Physical Trauma: Skin pain often arises from physical injuries such as cuts, burns, abrasions, and punctures. These injuries damage the skin’s tissues, activating pain receptors and triggering an inflammatory response.
- Temperature Extremes: Extreme heat or cold can cause skin pain. Excessive heat can lead to burns, while prolonged exposure to cold can result in frostbite. Both conditions damage skin cells and activate pain receptors.
- Chemicals: Certain chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and solvents, can irritate the skin and cause pain. Contact dermatitis, a common allergic reaction to substances like poison ivy, can also cause intense itching and pain.
- Radiation: Exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun can cause sunburn, leading to pain, redness, and inflammation.
- Mechanical Pressure: Prolonged pressure on the skin, such as from tight clothing or prolonged sitting, can cause discomfort and pain. This is particularly common in areas with limited blood flow.
- Insect Bites and Stings: Bites and stings from insects can inject venom or irritants into the skin, causing pain, swelling, and redness.
Internal Factors:
- Infections: Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can cause skin pain, redness, and inflammation. Examples include impetigo, cellulitis, herpes simplex, and tinea infections.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Autoimmune disorders, such as lupus and psoriasis, can trigger inflammation and pain in the skin.
- Neuropathic Pain: Damage to the nerves in the skin, often due to diabetes, shingles, or chemotherapy, can lead to chronic pain that is often burning, tingling, or stabbing in nature.
- Metabolic Disorders: Conditions like diabetes can affect the skin’s ability to heal properly, making it more susceptible to infections and pain.
- Cancer: Skin cancer, particularly melanoma, can cause pain, itching, and other symptoms.
- Psychological Factors: Stress, anxiety, and depression can lower pain thresholds, making individuals more sensitive to pain.
Common Skin Conditions Associated with Pain:
- Eczema: This chronic skin condition causes itchy, inflamed, and often painful patches of skin.
- Psoriasis: This autoimmune disorder causes red, scaly patches of skin that can be itchy and painful.
- Dermatitis: This general term encompasses various inflammatory skin conditions, including contact dermatitis and atopic dermatitis, both of which can cause pain and itching.
- Rosacea: This condition causes facial redness, flushing, and bumps that can be painful.
- Acne: While often associated with blemishes, acne can also cause painful inflammation and cysts.
Diagnosing the Cause of Skin Pain:
Determining the root cause of skin pain is crucial for effective treatment. A thorough medical history, physical examination, and sometimes laboratory tests are essential for diagnosis.
- Medical History: A detailed account of the onset, duration, location, and character of the pain, along with any other symptoms, provides valuable clues.
- Physical Examination: A visual inspection of the affected area, along with palpation (feeling the skin), helps identify any abnormalities, such as redness, swelling, or lesions.
- Laboratory Tests: Depending on the suspected cause, laboratory tests may be necessary to rule out infections, autoimmune disorders, or other underlying conditions.
Treatment Options for Skin Pain:
Treatment for skin pain depends on the underlying cause.
- Topical Medications: Creams, ointments, and lotions containing anti-inflammatory agents, corticosteroids, or antibiotics can help reduce inflammation and pain.
- Oral Medications: Pain relievers, antihistamines, or antibiotics may be prescribed to address pain, itching, or infections.
- Light Therapy: Phototherapy, using ultraviolet light, can be effective for conditions like psoriasis and eczema.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove growths, lesions, or infected tissue.
- Lifestyle Changes: Avoiding triggers, such as irritants or stress, can help manage pain and prevent flare-ups.
FAQs:
Q: What are some common triggers for skin pain?
A: Common triggers include exposure to extreme temperatures, irritants like chemicals or allergens, physical trauma, infections, and autoimmune disorders.
Q: When should I see a doctor about skin pain?
A: It is advisable to consult a doctor if the pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by other symptoms such as fever, chills, or swelling.
Q: Can skin pain be a sign of a serious condition?
A: Yes, skin pain can be a symptom of underlying conditions like infections, autoimmune disorders, or even cancer. It is crucial to seek medical attention for persistent or unexplained skin pain.
Tips for Managing Skin Pain:
- Keep the affected area clean and dry.
- Avoid scratching or picking at the skin.
- Apply cool compresses or ice packs to reduce inflammation.
- Take over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
- Wear loose-fitting clothing made of breathable fabrics.
- Avoid harsh soaps, detergents, and perfumes.
- Use a humidifier to keep the air moist, especially during winter.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques, such as yoga or meditation.
Conclusion:
Skin pain can be a complex and multifaceted symptom with a wide range of potential causes. Understanding the underlying mechanisms of skin pain is essential for effective diagnosis and treatment. While many cases of skin pain are relatively benign and resolve with simple measures, it is important to seek medical attention for persistent or severe pain, as it may indicate a more serious underlying condition. By understanding the causes and management strategies for skin pain, individuals can take proactive steps to alleviate discomfort and improve their overall well-being.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Causes of Skin Pain: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
