Understanding the T-Zone: A Guide to Oily Skin and Its Management
Related Articles: Understanding the T-Zone: A Guide to Oily Skin and Its Management
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the T-Zone: A Guide to Oily Skin and Its Management. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the T-Zone: A Guide to Oily Skin and Its Management

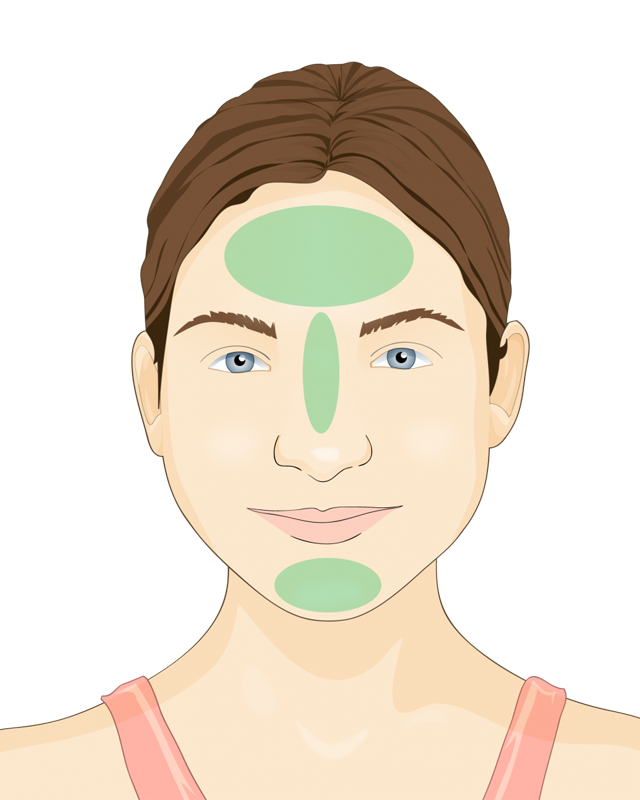
The T-zone, a region encompassing the forehead, nose, and chin, is often the focal point of oily skin concerns. This area is characterized by an increased production of sebum, a natural oil secreted by the skin’s sebaceous glands. While sebum serves a vital role in maintaining skin hydration and protecting it from environmental aggressors, an overproduction can lead to a range of issues, from shine and clogged pores to acne breakouts.
The Science Behind Oily Skin:
Sebum production is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including genetics, hormones, and environmental conditions.
- Genetics: Individuals with a predisposition to oily skin often inherit a tendency towards increased sebum production. This genetic inheritance dictates the size and activity of sebaceous glands, influencing the amount of oil secreted.
- Hormones: Hormones, particularly androgens, play a significant role in stimulating sebaceous gland activity. During puberty, hormonal fluctuations can lead to a surge in sebum production, contributing to the onset of acne in many adolescents. Hormonal imbalances later in life, such as during menstruation or pregnancy, can also trigger temporary increases in oiliness.
- Environmental Factors: External factors, such as humidity, temperature, and pollution, can further influence sebum production. Hot and humid environments can stimulate sweat glands, leading to increased sebum secretion. Pollution can clog pores, trapping sebum and exacerbating oiliness.
The Impact of Oily Skin:
While an overproduction of sebum can be a source of frustration, it is important to recognize that oily skin is not inherently problematic. However, excessive sebum can lead to:
- Shine: The excess oil creates a visible sheen on the skin, particularly in the T-zone.
- Clogged Pores: Sebum can accumulate in pores, blocking them and creating a breeding ground for bacteria.
- Acne Breakouts: Clogged pores can become inflamed, leading to the formation of pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads.
- Rough Texture: Excess oil can make the skin feel rough and uneven.
- Makeup Issues: Oily skin can make it difficult for makeup to stay in place, leading to smudging and caking.
Managing Oily Skin:
Managing oily skin requires a multi-faceted approach that addresses both the underlying causes and the symptoms.
1. Cleansing:
- Frequency: Cleansing twice daily, once in the morning and once in the evening, is essential for removing excess oil, dirt, and impurities.
- Product Selection: Opt for gentle, oil-free cleansers that are formulated for oily skin. Avoid harsh soaps or cleansers that can strip the skin of its natural oils and trigger further sebum production.
- Method: Use lukewarm water and avoid scrubbing or rubbing the skin aggressively. Gently massage the cleanser onto the skin and rinse thoroughly.
2. Exfoliation:
- Purpose: Exfoliation helps remove dead skin cells that can clog pores and contribute to breakouts.
- Frequency: Exfoliate 1-2 times a week, depending on skin sensitivity.
- Product Selection: Choose gentle exfoliating agents, such as chemical exfoliants containing salicylic acid or glycolic acid, or physical exfoliants with fine scrubs. Avoid harsh scrubs that can irritate the skin.
3. Toning:
- Purpose: Toners can help balance the skin’s pH, tighten pores, and remove any remaining traces of cleanser or makeup.
- Product Selection: Opt for alcohol-free toners that are specifically designed for oily skin. Look for ingredients like witch hazel, green tea, or aloe vera, which have astringent and calming properties.
4. Hydration:
- Importance: Despite the common misconception, oily skin still needs hydration. Dehydrated skin can trigger increased sebum production as the skin tries to compensate for the lack of moisture.
- Product Selection: Choose lightweight, oil-free moisturizers that are formulated for oily skin. Look for ingredients like hyaluronic acid, which attracts and retains moisture without clogging pores.
5. Sun Protection:
- Importance: Sun protection is crucial for all skin types, including oily skin. UV rays can damage the skin, leading to premature aging, hyperpigmentation, and even skin cancer.
- Product Selection: Choose oil-free, broad-spectrum sunscreens with an SPF of 30 or higher. Sunscreens specifically formulated for oily skin are often lightweight and non-comedogenic, meaning they won’t clog pores.
6. Diet:
- Impact: Diet can play a role in skin health, including sebum production.
- Recommendations: Avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive dairy consumption. Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
7. Lifestyle Factors:
- Stress Management: Stress can trigger hormonal imbalances that can lead to increased sebum production. Engage in stress-reducing activities, such as exercise, meditation, or yoga.
- Sleep: Adequate sleep is essential for overall health and skin regeneration. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night.
8. Professional Treatments:
- Facials: Professional facials designed for oily skin can help remove excess oil, unclog pores, and improve skin texture.
- Chemical Peels: Chemical peels use acids to exfoliate the skin and reduce oil production.
- Laser Treatments: Laser treatments can target sebaceous glands, reducing sebum production and improving skin texture.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: Is it okay to use oil-based products on oily skin?
A: It is generally not recommended to use oil-based products on oily skin. While some oils, such as jojoba oil, can be beneficial for certain skin types, they can contribute to clogged pores and exacerbate oiliness for those with oily skin.
Q: Can I use a clay mask on oily skin?
A: Clay masks can be beneficial for oily skin, as they absorb excess oil and impurities. However, it is important to choose a gentle clay mask and avoid overusing it, as excessive use can dry out the skin.
Q: How often should I wash my face with a facial cleanser?
A: It is generally recommended to cleanse the face twice daily, once in the morning and once in the evening. However, individuals with extremely oily skin may benefit from cleansing more frequently, such as after exercise or sweating.
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid when managing oily skin?
A: Common mistakes to avoid include:
- Over-washing: Over-washing can strip the skin of its natural oils and trigger further sebum production.
- Using harsh products: Harsh soaps, cleansers, or scrubs can irritate the skin and exacerbate oiliness.
- Skipping moisturizer: Oily skin still needs hydration. Skipping moisturizer can lead to dehydration and increased sebum production.
Tips for Managing Oily Skin:
- Blotting Papers: Use blotting papers to absorb excess oil throughout the day.
- Makeup Brushes: Clean your makeup brushes regularly to prevent the buildup of oil and bacteria.
- Hydrating Sprays: Use a hydrating spray to refresh the skin without adding oil.
- Water Intake: Drink plenty of water to keep the skin hydrated from within.
- Avoid Touching Your Face: Avoid touching your face unnecessarily, as this can transfer oil and bacteria.
Conclusion:
Oily skin, while often a source of concern, is a common skin type that can be effectively managed with the right approach. By understanding the causes of oily skin and implementing a consistent skincare routine, individuals can achieve a clear, balanced complexion. Remember, patience and persistence are key to managing oily skin and achieving long-term results.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the T-Zone: A Guide to Oily Skin and Its Management. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
