Understanding the Causes of Skin Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Causes of Skin Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Causes of Skin Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Causes of Skin Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide

Skin cancer, a prevalent and serious condition, arises from uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells within the skin. While its development is complex and influenced by a multitude of factors, understanding the key contributors is crucial for prevention and early detection. This comprehensive guide delves into the various elements that can contribute to the development of skin cancer, providing a thorough understanding of this widespread health concern.
The Sun: A Major Culprit
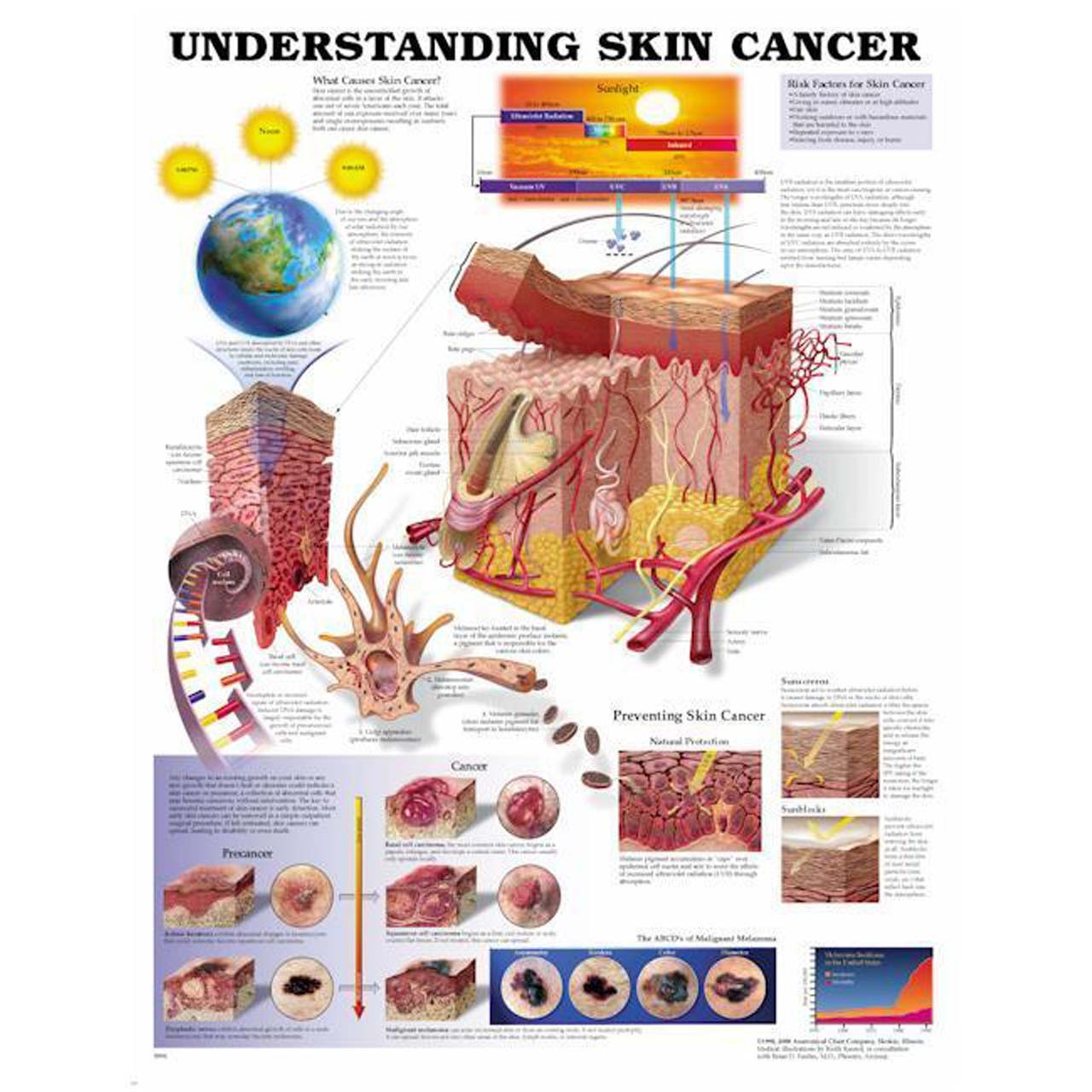
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is the most significant and widely recognized risk factor for skin cancer. UV rays, particularly UVB, damage DNA within skin cells, leading to mutations that can trigger uncontrolled growth. This damage accumulates over time, increasing the likelihood of developing skin cancer.
Factors Affecting Sun Exposure and Skin Cancer Risk:
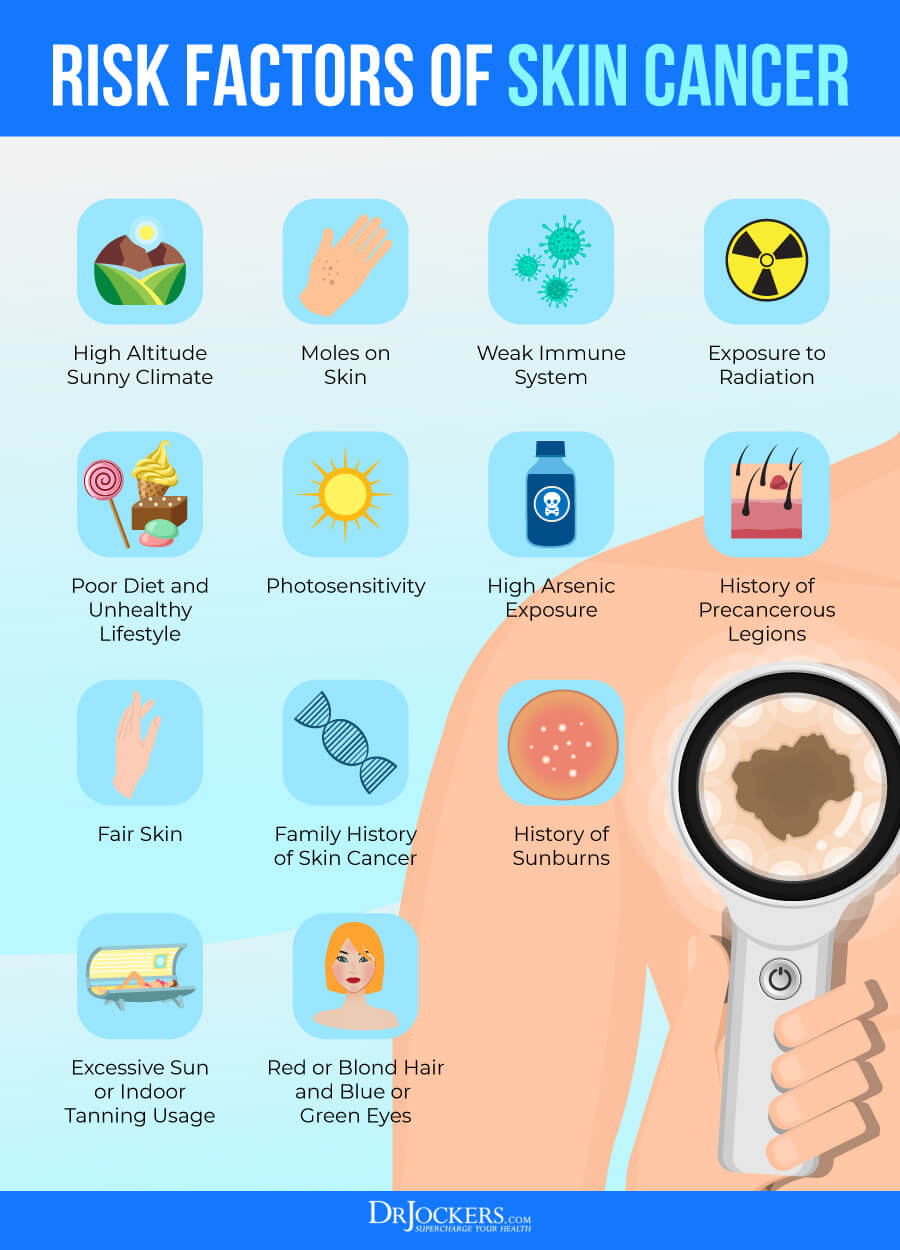
- Intensity of UV radiation: UV levels vary significantly based on geographic location, time of day, and season. Higher altitudes and areas closer to the equator experience more intense UV radiation.
- Duration of sun exposure: Prolonged exposure to UV radiation, even at lower intensities, can lead to cumulative damage and increase cancer risk.
- Skin type: Individuals with fair skin, freckles, and a history of sunburns are more susceptible to UV damage and subsequent skin cancer.
- Age: Skin cancer is more common in older individuals as they have accumulated more sun exposure over their lifetime.
Artificial Sources of UV Radiation:
- Tanning beds and sunlamps: These devices emit UV radiation, posing a significant risk of skin cancer. The World Health Organization classifies tanning beds as carcinogenic.
- Welding equipment: Certain types of welding equipment emit UV radiation, requiring protective measures for welders.
Beyond Sun Exposure: Other Contributing Factors
While sun exposure is a primary driver, other factors can influence the development of skin cancer:
Genetic Predisposition:
- Family history: A family history of skin cancer increases an individual’s risk. Genetic mutations can predispose individuals to the disease.
- Certain syndromes: Individuals with genetic syndromes, such as xeroderma pigmentosum, are highly susceptible to skin cancer due to impaired DNA repair mechanisms.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors:
- Smoking: Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of certain types of skin cancer, including squamous cell carcinoma.
- Exposure to certain chemicals: Exposure to certain chemicals, such as arsenic and coal tar, can increase the risk of skin cancer.
- Weakened immune system: Individuals with weakened immune systems, due to conditions like HIV/AIDS or organ transplantation, are more vulnerable to skin cancer.
- Viral infections: Certain viral infections, such as human papillomavirus (HPV), have been linked to an increased risk of skin cancer.
Skin Cancer Types and Their Causes:
Skin cancer is categorized into three main types:
- Basal cell carcinoma (BCC): The most common type, BCC typically appears as a pearly or waxy bump. It usually arises from sun-exposed areas and is rarely fatal.
- Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): SCC is more aggressive than BCC and can metastasize if left untreated. It often presents as a firm, red nodule or a scaly, crusted patch.
- Melanoma: The most serious type, melanoma develops from melanocytes, the cells responsible for skin pigmentation. It can arise from existing moles or appear as a new growth. Melanoma is highly aggressive and can spread rapidly if not detected early.
Understanding the Importance of Prevention and Early Detection
While skin cancer can be caused by a variety of factors, understanding the role of UV radiation and other contributing elements is paramount for effective prevention and early detection.
Prevention Strategies:
- Limit sun exposure: Seek shade during peak UV hours (10 am to 4 pm), wear protective clothing, and use broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
- Avoid tanning beds and sunlamps: These devices emit harmful UV radiation and should be avoided entirely.
- Regular skin exams: Conduct self-exams regularly to identify any changes in skin appearance. Seek professional dermatological exams at least once a year.
- Healthy lifestyle choices: Maintain a healthy weight, eat a balanced diet, and avoid smoking to reduce overall cancer risk.
Early Detection: A Key to Successful Treatment
Early detection is critical for successful skin cancer treatment. The earlier a skin cancer is diagnosed and treated, the better the chances of a complete cure.
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For:
- Changes in moles: Look for changes in size, shape, color, or texture of existing moles.
- New growths: Pay attention to any new bumps, sores, or growths on the skin.
- Sores that don’t heal: Any sores that don’t heal within a few weeks should be examined by a doctor.
- Changes in skin texture: Look for changes in the texture of the skin, such as thickening, scaling, or roughness.
- Unusual bleeding or itching: Any unusual bleeding or itching from the skin should be investigated.
Seeking Professional Help:
If you notice any of these signs or symptoms, consult a dermatologist promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment significantly improve the chances of successful recovery.
FAQs
Q: Can skin cancer be prevented entirely?
A: While it is impossible to eliminate all risk factors for skin cancer, adhering to preventive measures can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing the disease. Limiting sun exposure, avoiding tanning beds, and practicing regular skin exams are crucial steps in minimizing risk.
Q: Is skin cancer contagious?
A: Skin cancer is not contagious and cannot be spread from person to person.
Q: Can anyone get skin cancer?
A: While certain individuals are at higher risk due to genetic predisposition or lifestyle factors, anyone can develop skin cancer.
Q: Can skin cancer be cured?
A: The curability of skin cancer depends on the type, stage, and location of the cancer. Early detection and treatment significantly increase the chances of a complete cure.
Q: What are the treatment options for skin cancer?
A: Treatment options for skin cancer vary depending on the type, size, and location of the cancer. Common treatment methods include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy.
Tips for Reducing Skin Cancer Risk:
- Wear protective clothing: Cover as much skin as possible with long-sleeved shirts, pants, hats, and sunglasses.
- Apply sunscreen liberally and frequently: Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher and reapply every two hours, especially after swimming or sweating.
- Avoid peak UV hours: Limit outdoor activities during the hours of 10 am to 4 pm when UV radiation is most intense.
- Check your skin regularly: Conduct self-exams monthly to identify any changes in skin appearance.
- See a dermatologist annually: Regular professional skin exams can help detect skin cancer early when it is most treatable.
Conclusion:
Skin cancer is a complex disease with multiple contributing factors. While sun exposure is the primary driver, genetic predisposition, lifestyle choices, and environmental factors also play a role. By understanding the causes, implementing preventive measures, and practicing early detection, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing skin cancer. Early detection and treatment are essential for successful outcomes, emphasizing the importance of regular skin exams and seeking professional advice promptly if any concerning changes are noticed.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-skin-cancer-3010808_final-743e4e72b4164bedacb08eedbd9c52c7.png)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Causes of Skin Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
