Understanding HS Skin: A Comprehensive Guide to Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Related Articles: Understanding HS Skin: A Comprehensive Guide to Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding HS Skin: A Comprehensive Guide to Hidradenitis Suppurativa. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding HS Skin: A Comprehensive Guide to Hidradenitis Suppurativa

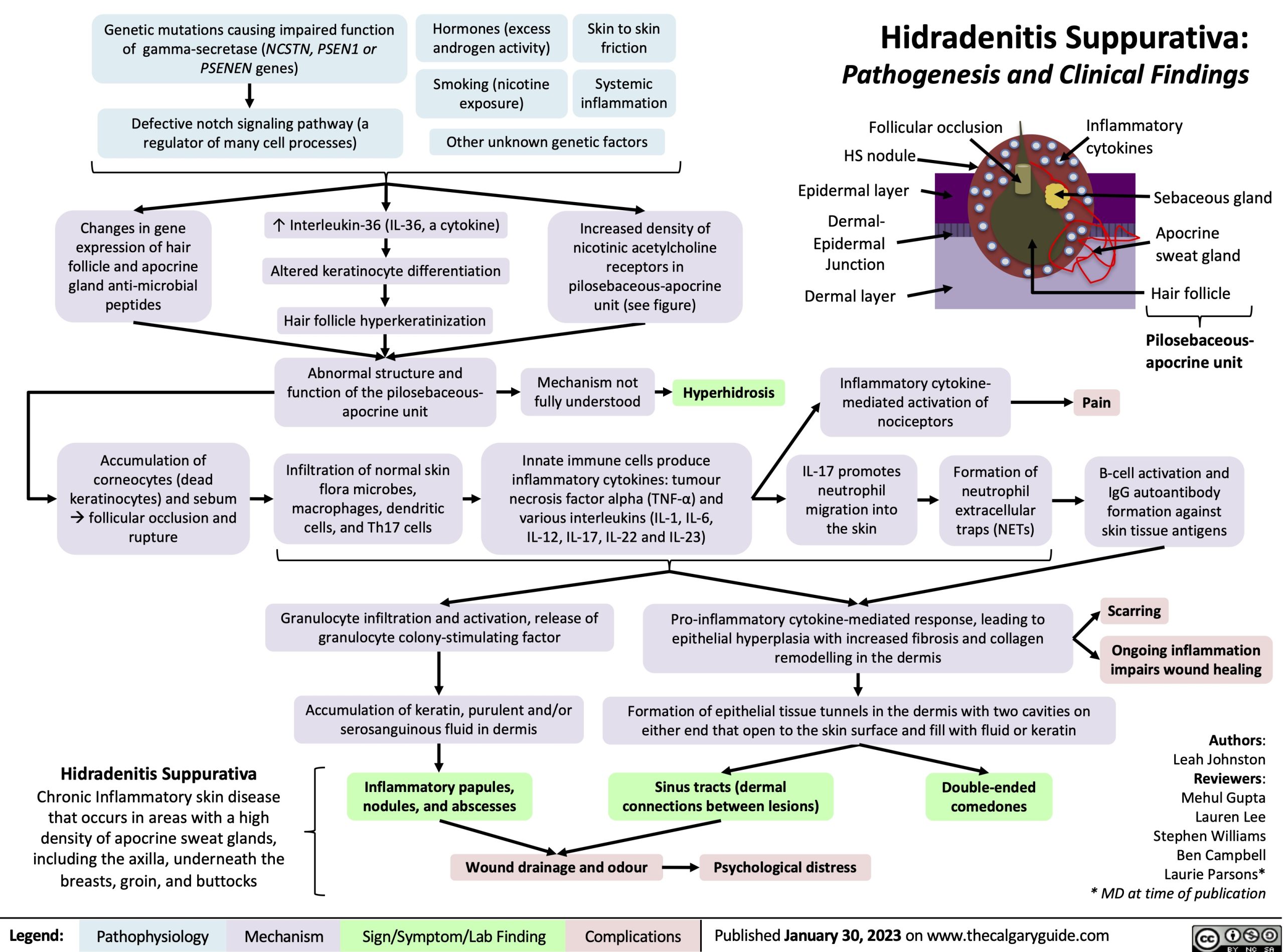
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), often referred to as "acne inversa," is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that affects the apocrine sweat glands, primarily found in areas with a high concentration of these glands, such as the armpits, groin, buttocks, and breasts. Characterized by painful, recurring boils and abscesses, HS can significantly impact an individual’s physical, emotional, and social well-being.
The Nature of HS Skin
HS is not a simple skin infection but a complex, chronic condition. Its underlying cause remains unclear, but several factors are believed to contribute to its development, including:
- Genetics: A family history of HS increases the risk of developing the condition.
- Hormones: Fluctuations in hormone levels, particularly during puberty, menstruation, and pregnancy, can trigger or worsen HS.
- Friction and Trauma: Repeated rubbing or irritation in affected areas can exacerbate HS symptoms.
- Smoking: Smoking is a significant risk factor for HS and can worsen its severity.
- Obesity: Individuals with obesity are more likely to develop HS, and the condition may be more severe in this population.
Understanding the Pathophysiology
The exact mechanisms driving HS are still being investigated, but current research points to a complex interplay of factors:
- Follicular occlusion: Hair follicles in affected areas become blocked, leading to the formation of inflammatory nodules and cysts.
- Immune dysregulation: An overactive immune response plays a crucial role in the development of HS lesions.
- Inflammation and scarring: Chronic inflammation leads to the formation of deep, draining sinuses and scars, which can further complicate the condition.
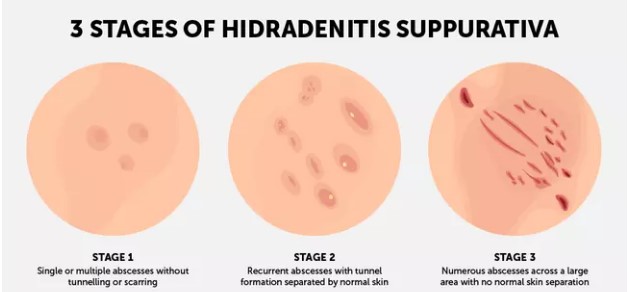
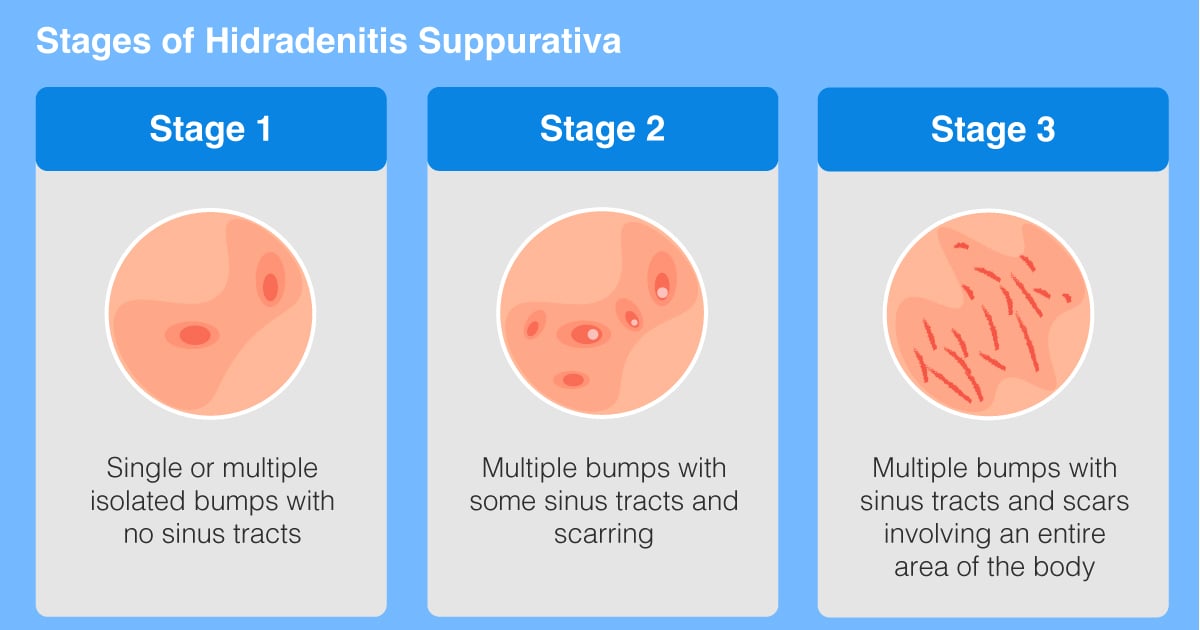
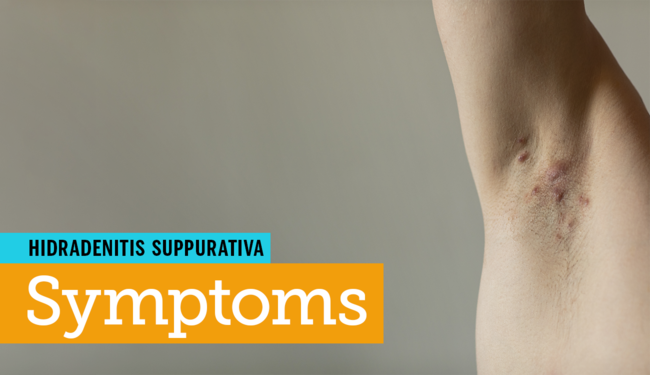
Symptoms and Diagnosis
HS symptoms can vary in severity and frequency. Some individuals may experience only occasional, mild outbreaks, while others may experience chronic, severe disease. Common symptoms include:
- Painful, inflamed nodules: These nodules can be small and tender or large and deeply painful.
- Abscesses: These are collections of pus that form under the skin and can burst, releasing foul-smelling drainage.
- Sinuses: These are tunnels or tracts that form beneath the skin and can drain pus or fluid.
- Scarring: Chronic inflammation can lead to scarring, which can be disfiguring and limit mobility.
Diagnosis of HS typically involves a physical examination by a dermatologist. The doctor will assess the patient’s symptoms, examine the lesions, and consider the patient’s medical history. In some cases, a biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options
HS is a challenging condition to treat, and there is no cure. However, various treatment options can help manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and improve quality of life. These options include:
- Topical medications: Antibiotics, antiseptics, and other topical medications can help control inflammation and infection.
- Oral medications: Antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and hormonal therapies can be used to manage HS symptoms.
- Biologic therapies: These medications target specific immune pathways involved in the development of HS and can be effective in reducing inflammation and improving symptoms.
- Surgical procedures: In some cases, surgical procedures may be necessary to drain abscesses, remove scar tissue, or reduce the size of lesions.
- Lifestyle modifications: Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding smoking, and managing stress can help prevent HS flare-ups.
The Impact of HS
HS can have a profound impact on an individual’s life, affecting their:
- Physical health: The pain and discomfort associated with HS can limit mobility and affect daily activities.
- Emotional well-being: The chronic nature of HS, along with the associated stigma, can lead to anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem.
- Social life: HS can affect relationships, career choices, and participation in social activities.
Managing HS: A Holistic Approach
Managing HS effectively requires a multidisciplinary approach involving:
- Dermatologist: A dermatologist can diagnose HS, recommend appropriate treatment options, and monitor progress.
- Primary care physician: A primary care physician can manage any underlying health conditions that may contribute to HS.
- Mental health professional: A therapist or counselor can provide support and coping strategies to manage the emotional impact of HS.
- Support groups: Connecting with others who have HS can provide valuable support, information, and encouragement.
FAQs about HS Skin
1. Is HS contagious?
No, HS is not contagious. It is not caused by a virus or bacteria that can spread from person to person.
2. What causes HS?
The exact cause of HS is unknown, but it is believed to be a complex interplay of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors.
3. Can HS be prevented?
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent HS, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding smoking, and managing stress may reduce the risk of developing the condition.
4. Can HS be cured?
Currently, there is no cure for HS. However, various treatment options can help manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and improve quality of life.
5. What is the best treatment for HS?
The best treatment for HS depends on the severity of the condition and the individual’s response to therapy. A dermatologist can recommend the most appropriate treatment plan.
Tips for Managing HS
- Practice good hygiene: Wash affected areas with mild soap and water twice a day.
- Avoid tight clothing: Wear loose-fitting, breathable clothing to minimize friction and irritation.
- Moisturize regularly: Use a gentle moisturizer to keep the skin hydrated and prevent dryness.
- Manage stress: Stress can trigger HS flare-ups, so finding healthy ways to manage stress is important.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity can worsen HS, so maintaining a healthy weight is beneficial.
- Quit smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for HS and can worsen its severity.
- Seek support: Join a support group or connect with others who have HS to share experiences and find support.
Conclusion
HS is a chronic, debilitating skin disease that significantly impacts an individual’s physical, emotional, and social well-being. While there is no cure for HS, various treatment options can help manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and improve quality of life. A multidisciplinary approach involving a dermatologist, primary care physician, mental health professional, and support groups is essential for effective management of HS. By understanding the condition, seeking appropriate treatment, and adopting healthy lifestyle practices, individuals with HS can live fulfilling lives despite the challenges posed by this complex disease.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding HS Skin: A Comprehensive Guide to Hidradenitis Suppurativa. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
