Understanding Acne: A Comprehensive Guide to Causes, Treatment, and Management
Related Articles: Understanding Acne: A Comprehensive Guide to Causes, Treatment, and Management
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Acne: A Comprehensive Guide to Causes, Treatment, and Management. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Acne: A Comprehensive Guide to Causes, Treatment, and Management
Acne vulgaris, commonly known as acne, is a prevalent skin condition affecting a significant portion of the population, particularly during adolescence and young adulthood. It manifests as blemishes, pimples, and other inflammatory lesions on the skin, primarily on the face, neck, chest, back, and shoulders. While often perceived as a superficial concern, acne can significantly impact an individual’s self-esteem and social interactions. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of acne, delving into its causes, mechanisms, treatment options, and strategies for effective management.
The Complexities of Acne Formation
Acne is not a simple skin condition; it arises from a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Hormonal Fluctuations: During puberty, adolescence, and even during the menstrual cycle, hormonal fluctuations, particularly in androgen levels, can stimulate sebaceous glands, leading to increased sebum production. Sebum is an oily substance that lubricates the skin, but excessive production can clog pores.
- Hyperkeratinization: The skin’s natural shedding process, known as keratinization, can become irregular in individuals prone to acne. This leads to an accumulation of dead skin cells within the hair follicles, further contributing to pore blockage.
- Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes): This bacterium, commonly found on the skin, thrives in the oily environment of clogged pores. It produces inflammatory substances that trigger the inflammatory response characteristic of acne.
- Inflammation: The body’s immune system, attempting to combat the bacteria and trapped sebum, triggers inflammation, leading to redness, swelling, and the formation of papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts.
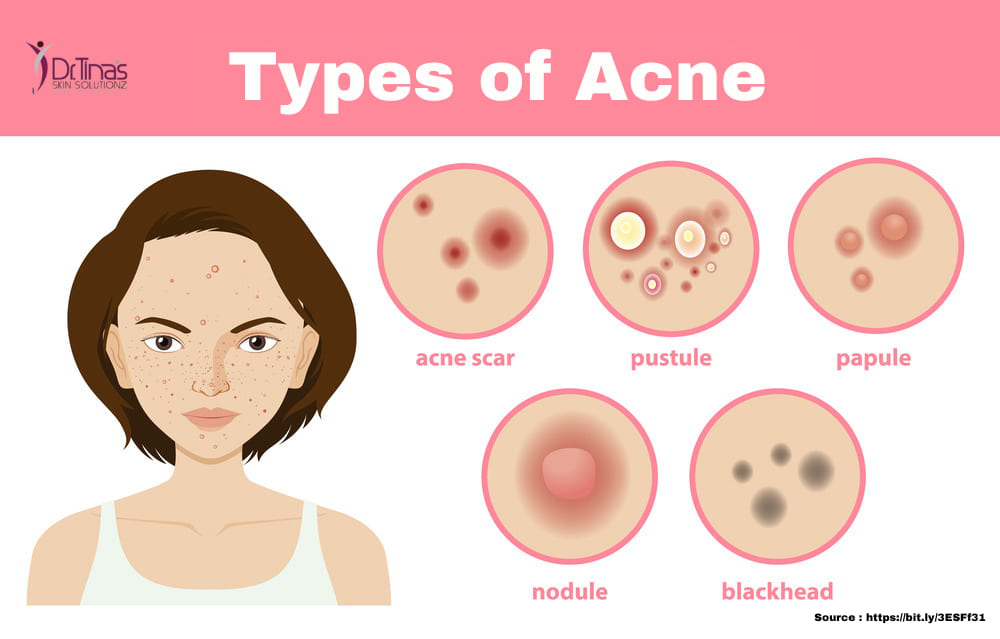
Acne Lesions: A Closer Look
Acne lesions are classified based on their severity and appearance:
- Comedones: These are the most common type of acne lesion, appearing as blackheads or whiteheads. Blackheads are open comedones, where the trapped sebum oxidizes and turns dark. Whiteheads are closed comedones, where the sebum remains trapped under the skin’s surface.
- Papules: Small, red, inflamed bumps that are firm to the touch.
- Pustules: Papules that develop a white or yellow pus-filled center.
- Nodules: Large, inflamed, and painful lesions that extend deep into the skin.
- Cysts: Large, pus-filled lesions that can cause scarring.
Acne Severity: From Mild to Severe
The severity of acne is typically classified based on the number and type of lesions present:
- Mild acne: Primarily characterized by comedones, with occasional papules or pustules.
- Moderate acne: Marked by an increased number of papules, pustules, and possibly some nodules.
- Severe acne: Characterized by numerous inflammatory lesions, including nodules and cysts, often leading to scarring.
Treatment Strategies: A Multifaceted Approach
Treating acne effectively requires a multi-faceted approach, often involving a combination of topical and oral medications, as well as lifestyle modifications:
-
Topical Medications:
- Benzoyl peroxide: This over-the-counter (OTC) medication kills P. acnes and helps reduce inflammation.
- Salicylic acid: An exfoliating agent that helps unclog pores and remove dead skin cells.
- Retinoids: Vitamin A derivatives that regulate cell growth and reduce sebum production.
- Sulfur: An anti-inflammatory agent that also helps dry out excess sebum.
- Azelaic acid: An anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial agent that reduces redness and inflammation.
-
Oral Medications:
- Antibiotics: Used to fight P. acnes and reduce inflammation.
- Oral contraceptives: Can be effective for women with acne related to hormonal fluctuations.
- Isotretinoin (Accutane): A potent oral retinoid that is highly effective in treating severe, recalcitrant acne. It has potential side effects and requires careful monitoring.
-
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Gentle skin care: Avoid harsh scrubbing, excessive washing, and products that irritate the skin.
- Proper cleansing: Wash your face twice daily with a gentle cleanser, avoiding harsh soaps.
- Moisturizing: Use a non-comedogenic moisturizer to keep the skin hydrated.
- Sunscreen: Protect your skin from the sun, as it can worsen acne and increase the risk of scarring.
- Diet: While a specific acne diet has not been scientifically proven, some individuals may find that reducing their intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and dairy products can help.
- Stress management: Stress can exacerbate acne. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing can help manage stress levels.
Acne and Scarring: A Persistent Challenge
Acne can leave behind scars, which can be both physically and emotionally distressing. Scarring occurs when the deeper layers of the skin are damaged, leading to an uneven surface. There are various types of acne scars:
- Ice pick scars: Narrow, deep scars that resemble ice pick marks.
- Boxcar scars: Wide, depressed scars with sharp edges.
- Rolling scars: Broad, shallow scars that cause a wave-like appearance.
- Hypertrophic scars: Raised, thick scars that can be itchy and painful.
- Keloid scars: Large, raised scars that extend beyond the original wound area.
Treatment options for acne scars include:
- Topical treatments: Retinoids, chemical peels, and laser therapy can help improve the appearance of scars.
- Fillers: Injections of hyaluronic acid or other fillers can plump up depressed scars.
- Subcision: A procedure that releases scar tissue beneath the skin.
- Laser resurfacing: Uses lasers to remove the top layer of skin, promoting new skin growth.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
Q: What is the best way to prevent acne?
A: While there is no foolproof method to completely prevent acne, maintaining a consistent skin care routine, avoiding harsh products, and managing stress can significantly reduce the risk of breakouts.
Q: Can acne be cured?
A: Acne is often a chronic condition, meaning it can flare up periodically. However, with proper treatment and management, it can be effectively controlled and its severity reduced.
Q: Is acne contagious?
A: Acne is not contagious. It is caused by a combination of factors specific to each individual.
Q: Can certain foods trigger acne?
A: While there is no definitive evidence that specific foods cause acne, some individuals may find that reducing their intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and dairy products can help manage breakouts.
Q: What should I do if my acne is severe or not responding to treatment?
A: If you are experiencing severe acne or if your current treatment is not effective, it is essential to consult a dermatologist. They can provide a personalized treatment plan and address any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to your acne.
Tips for Effective Acne Management
- Be patient: Acne treatment takes time, and results may not be immediate. Consistency is key.
- Don’t pick or squeeze your pimples: This can worsen inflammation and increase the risk of scarring.
- Avoid harsh soaps and scrubs: These can irritate the skin and worsen acne.
- Use non-comedogenic products: Choose products that are specifically designed for acne-prone skin.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water to keep your skin hydrated.
- Get enough sleep: Sleep deprivation can worsen acne.
- Manage stress: Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, meditation, or spending time in nature.
Conclusion: A Journey Towards Clearer Skin
Acne is a common skin condition that can be frustrating and impact self-esteem. However, with proper understanding, effective treatment, and consistent management, it is possible to achieve clearer skin and reduce the impact of acne on your life. Remember, seeking professional guidance from a dermatologist is crucial, especially for severe acne or when over-the-counter treatments are ineffective. By taking a comprehensive approach to skin care, you can embark on a journey towards healthier, clearer skin.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Acne: A Comprehensive Guide to Causes, Treatment, and Management. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
