The Vital Connection: Vitamin D and Skin Health
Related Articles: The Vital Connection: Vitamin D and Skin Health
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Vital Connection: Vitamin D and Skin Health. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Vital Connection: Vitamin D and Skin Health

Vitamin D, often referred to as the "sunshine vitamin," plays a multifaceted role in human health, extending beyond its well-known contribution to bone health. Emerging research increasingly highlights the crucial connection between vitamin D and skin health, revealing its significant impact on various aspects of skin function and appearance.
Vitamin D: A Skin-Deep Influence
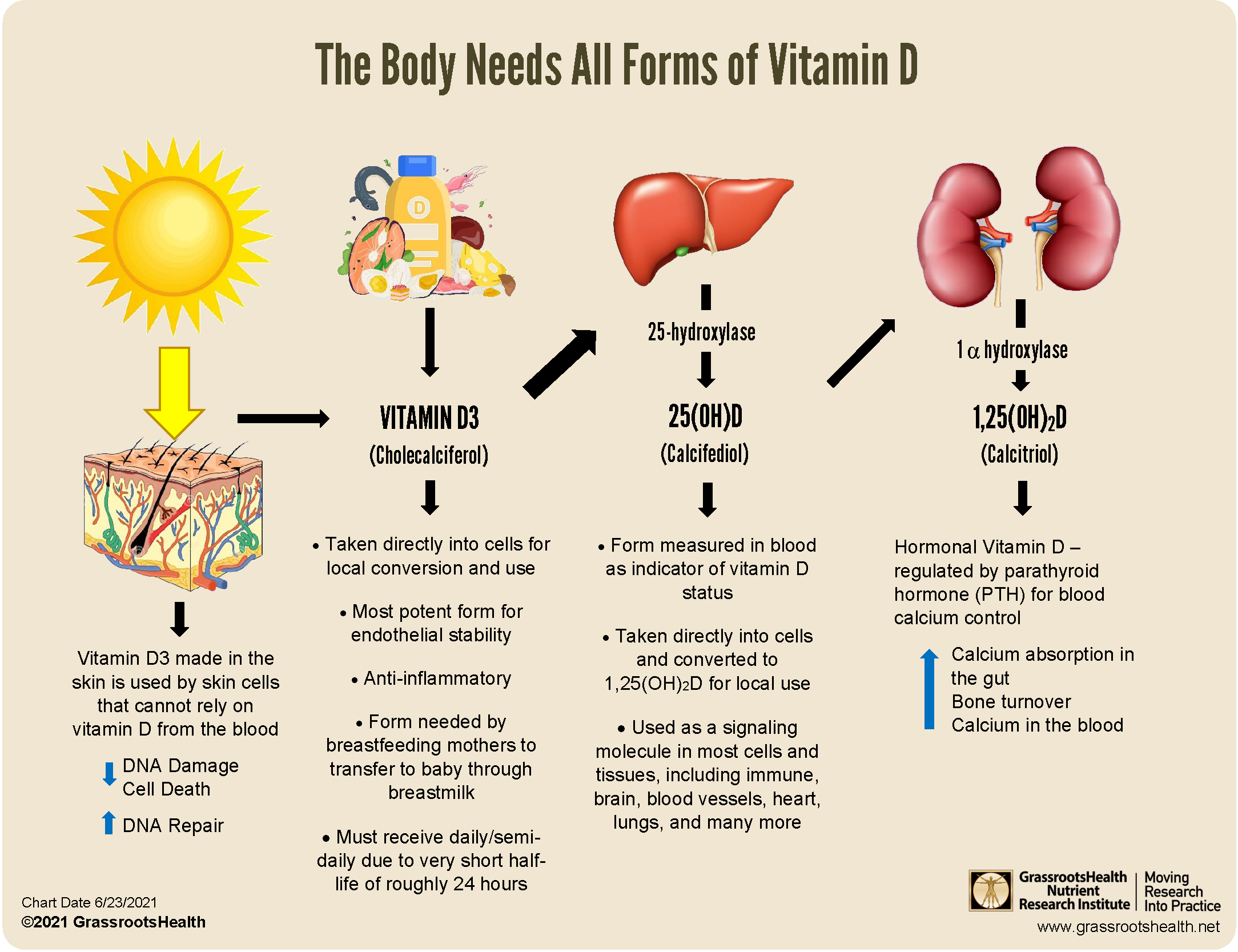
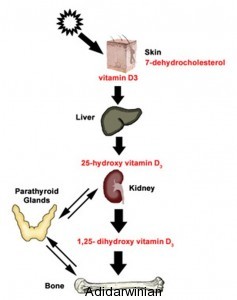
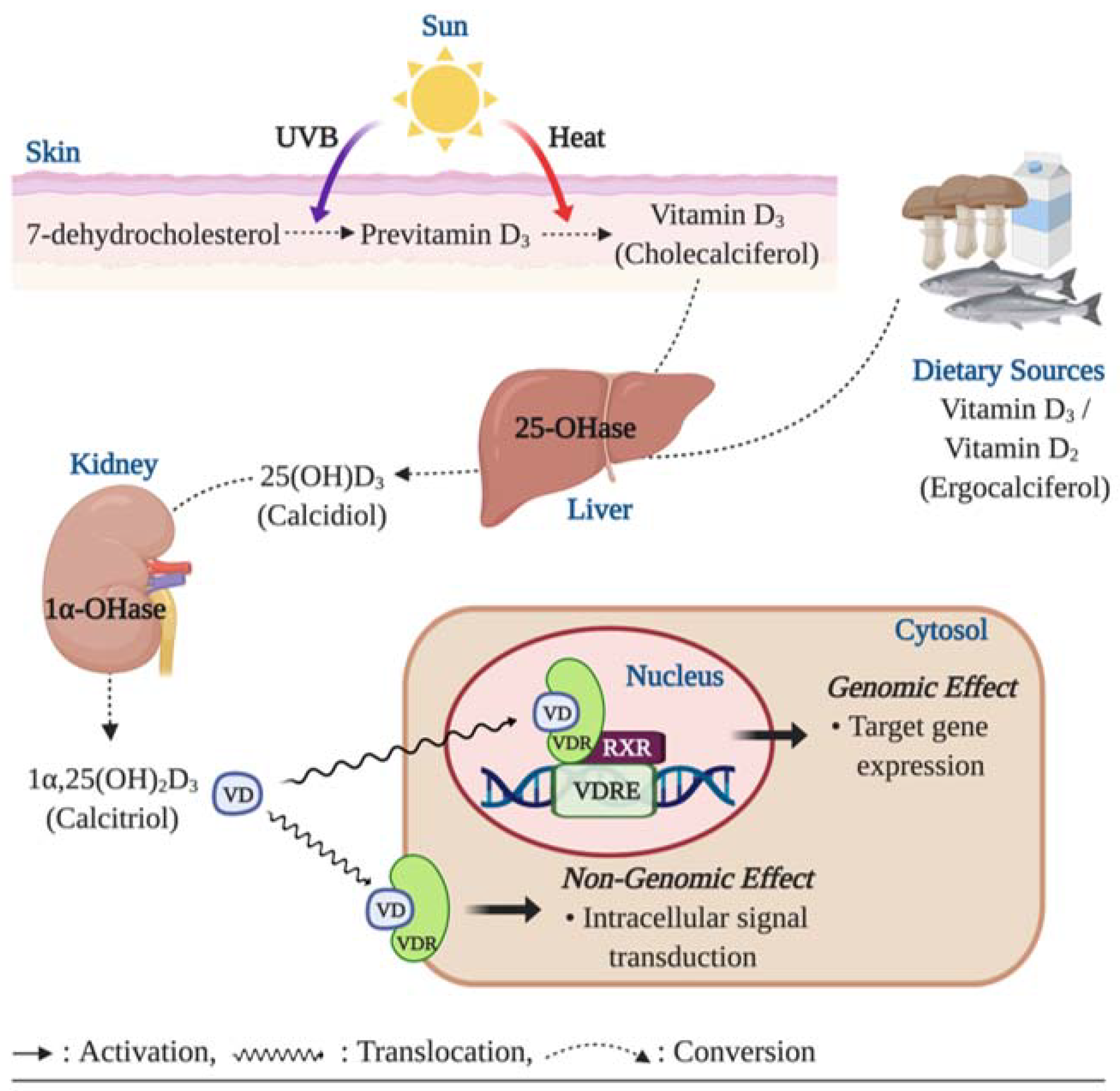
Vitamin D, a fat-soluble vitamin, is synthesized in the skin upon exposure to ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation from sunlight. This process, known as cutaneous vitamin D synthesis, is a primary source of vitamin D for most individuals. However, factors such as skin pigmentation, latitude, seasonality, and clothing choices can influence the body’s ability to produce sufficient vitamin D through this mechanism.
Beyond its role in calcium absorption and bone health, vitamin D exerts a profound influence on skin health through various mechanisms. It functions as a powerful modulator of cellular processes, influencing cell growth, differentiation, and immune responses within the skin.
Vitamin D’s Benefits for Skin Health
-
Protection Against Skin Cancer: Research suggests that adequate vitamin D levels may play a role in reducing the risk of developing certain skin cancers, particularly melanoma. While sunlight exposure is a key factor in vitamin D production, it also poses a risk of skin cancer. Maintaining sufficient vitamin D levels through sun-safe practices and dietary supplementation can offer a potential protective effect.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Vitamin D exhibits anti-inflammatory properties, helping to regulate the immune response in the skin. This can be beneficial in conditions like psoriasis, eczema, and acne, where inflammation plays a significant role.
-
Wound Healing and Repair: Vitamin D promotes wound healing by stimulating the production of collagen, a crucial protein for skin structure and repair. It also enhances the activity of immune cells involved in wound healing, contributing to faster and more efficient tissue regeneration.
-
Skin Barrier Function: Vitamin D strengthens the skin’s barrier function, which protects against environmental stressors such as allergens, irritants, and pathogens. This barrier function helps maintain skin hydration, reduce dryness, and prevent inflammation.
-
Antioxidant Defense: Vitamin D acts as an antioxidant, protecting the skin from damage caused by free radicals. These damaging molecules, generated by environmental factors like UV radiation and pollution, contribute to skin aging and other skin problems.
Vitamin D Deficiency and Skin Health
Insufficient vitamin D levels, a condition known as vitamin D deficiency, can negatively impact skin health. Studies have linked vitamin D deficiency to:
-
Increased Risk of Skin Cancer: Some research suggests that low vitamin D levels may be associated with an increased risk of skin cancer, particularly melanoma. However, further research is needed to establish a definitive link.
-
Exacerbation of Skin Conditions: Vitamin D deficiency can exacerbate pre-existing skin conditions such as psoriasis, eczema, and acne. This is attributed to its role in regulating inflammation and immune responses.
-
Slowed Wound Healing: Insufficient vitamin D levels can impair wound healing due to its role in collagen production and immune cell activation.
-
Skin Aging: Vitamin D’s antioxidant properties help protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals. Deficiency in vitamin D can accelerate skin aging and contribute to wrinkles, fine lines, and loss of elasticity.
Factors Affecting Vitamin D Levels
Several factors can influence vitamin D levels, including:
-
Skin Pigmentation: Individuals with darker skin pigmentation have lower vitamin D synthesis rates due to melanin’s absorption of UVB radiation.
-
Latitude: People living in higher latitudes, where sunlight is weaker, are more likely to experience vitamin D deficiency.
-
Seasonality: Vitamin D production is higher during summer months when sunlight is stronger and less clothing is worn.
-
Clothing and Sunscreen Use: Wearing clothing that covers the skin and using sunscreen, while essential for sun protection, can reduce vitamin D synthesis.
-
Age: Vitamin D synthesis declines with age, making older adults more susceptible to deficiency.
-
Dietary Intake: While sunlight exposure is the primary source of vitamin D, some foods, such as fatty fish, eggs, and fortified milk, contain vitamin D.
Addressing Vitamin D Deficiency
Addressing vitamin D deficiency involves a combination of strategies:
-
Sunlight Exposure: Safe sun exposure, without burning, can increase vitamin D production. However, it is crucial to practice sun safety by limiting exposure during peak hours, wearing protective clothing, and using sunscreen.
-
Dietary Intake: Consuming vitamin D-rich foods can contribute to maintaining adequate levels.
-
Supplementation: Vitamin D supplements are available in various forms, including vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol). Consultation with a healthcare professional is recommended to determine the appropriate dosage and type of supplement.
FAQs About Vitamin D and Skin Health
Q: Can vitamin D help with acne?
A: While research suggests that vitamin D may have anti-inflammatory effects that could potentially benefit acne, further studies are needed to confirm its effectiveness.
Q: Can vitamin D help with psoriasis?
A: Some studies have shown that vitamin D supplementation can improve symptoms of psoriasis, such as redness, scaling, and itching. However, more research is needed to establish its long-term efficacy and optimal dosage.
Q: Can vitamin D help with eczema?
A: Preliminary research suggests that vitamin D may have a role in improving eczema symptoms, but more studies are required to confirm its effectiveness.
Q: Can vitamin D help with skin cancer prevention?
A: While research suggests that adequate vitamin D levels may play a role in reducing the risk of certain skin cancers, particularly melanoma, it is crucial to remember that sun exposure is a major risk factor for skin cancer. Maintaining sufficient vitamin D levels through sun-safe practices and dietary supplementation should be considered as part of a comprehensive skin cancer prevention strategy.
Tips for Maintaining Healthy Vitamin D Levels
-
Safe Sun Exposure: Aim for 10-15 minutes of sun exposure on most days of the week, during non-peak hours, to allow for vitamin D synthesis without risking sunburn.
-
Dietary Intake: Include vitamin D-rich foods like fatty fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel), eggs, and fortified milk in your diet.
-
Supplementation: Consult with a healthcare professional to determine if vitamin D supplementation is necessary based on your individual needs and risk factors.
-
Regular Blood Tests: Regular blood tests can help monitor vitamin D levels and ensure adequate intake.
-
Sun Safety Practices: Always protect your skin from the sun’s harmful rays by wearing protective clothing, hats, and sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
Conclusion
Vitamin D plays a vital role in maintaining healthy skin, influencing various aspects of skin function and appearance. Adequate vitamin D levels contribute to protection against skin cancer, regulation of inflammation, wound healing, skin barrier function, and antioxidant defense. Vitamin D deficiency, on the other hand, can negatively impact skin health, potentially increasing the risk of skin cancer, exacerbating existing skin conditions, slowing wound healing, and accelerating skin aging. Maintaining sufficient vitamin D levels through safe sun exposure, dietary intake, and supplementation, when necessary, is essential for promoting optimal skin health. Regular blood tests can help monitor vitamin D levels and ensure adequate intake. It is important to remember that while vitamin D plays a significant role in skin health, it is not a substitute for sun safety practices, which remain crucial for preventing skin cancer and protecting the skin from sun damage.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Vital Connection: Vitamin D and Skin Health. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
