The Sun’s Embrace: A Guide to Understanding Sunscreen and its Crucial Role in Skin Health
Related Articles: The Sun’s Embrace: A Guide to Understanding Sunscreen and its Crucial Role in Skin Health
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Sun’s Embrace: A Guide to Understanding Sunscreen and its Crucial Role in Skin Health. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Sun’s Embrace: A Guide to Understanding Sunscreen and its Crucial Role in Skin Health
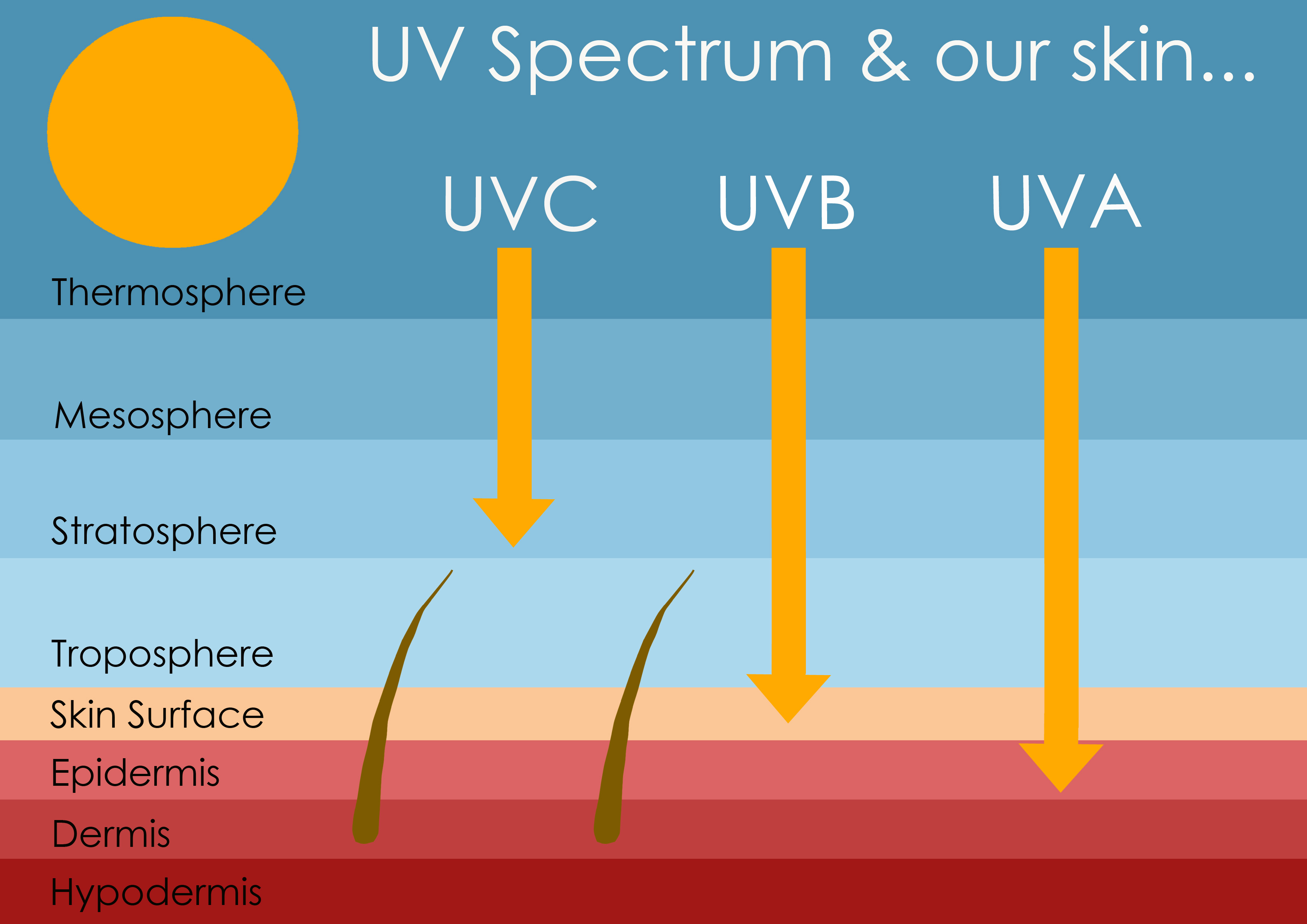
The sun, a celestial body that sustains life on Earth, also harbors a hidden threat – ultraviolet (UV) radiation. While vital for photosynthesis and vitamin D production, excessive exposure to UV rays can have detrimental effects on human skin, leading to sunburn, premature aging, and an increased risk of skin cancer. This underscores the importance of understanding and embracing the protective shield offered by sunscreen.
The Science of Sunscreen: A Protective Barrier Against the Sun’s Harmful Rays
Sunscreen, a topical product designed to absorb or reflect UV radiation, serves as a crucial defense mechanism against the sun’s damaging effects. It works by creating a physical barrier that prevents UV rays from penetrating the skin, thereby minimizing their impact.
Understanding the Types of UV Radiation
The sun emits two primary types of UV radiation:
- UVA (Ultraviolet A): Penetrates the deeper layers of the skin, contributing to premature aging, wrinkles, and hyperpigmentation (dark spots).
- UVB (Ultraviolet B): Primarily responsible for sunburns, skin cancer, and the breakdown of collagen, leading to premature aging.
Sunscreen Ingredients: The Key to Effective Protection
Sunscreens contain specific ingredients that either absorb or reflect UV radiation. These ingredients fall into two primary categories:
- Chemical Filters: These ingredients absorb UV radiation and release it as heat. Common examples include oxybenzone, octinoxate, avobenzone, and octisalate.
- Mineral Filters: These ingredients act as physical blockers, reflecting UV rays away from the skin. The most common mineral filters are zinc oxide and titanium dioxide.
The Sun Protection Factor (SPF): A Measure of Protection
The Sun Protection Factor (SPF) is a numerical rating that indicates how long a sunscreen will protect the skin from UVB radiation compared to unprotected skin. For example, an SPF 30 sunscreen provides 30 times more protection against UVB radiation than no sunscreen.
The Importance of Broad Spectrum Protection
It is crucial to choose sunscreens that offer broad spectrum protection, meaning they protect against both UVA and UVB rays. This ensures comprehensive defense against the sun’s full spectrum of harmful radiation.
Beyond Sunburns: The Long-Term Consequences of Sun Exposure
While sunburns are a visible and immediate consequence of excessive sun exposure, the long-term effects are far more insidious. Over time, prolonged sun exposure can lead to:
- Premature Aging: Sun damage breaks down collagen and elastin, the proteins responsible for skin elasticity, resulting in wrinkles, fine lines, and sagging skin.
- Skin Cancer: UV radiation can damage DNA in skin cells, leading to the development of various skin cancers, including melanoma, the deadliest form.
- Hyperpigmentation: Sun exposure can trigger the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color, leading to dark spots, freckles, and uneven skin tone.
The Benefits of Sunscreen: A Shield for Skin Health
Regular sunscreen use offers numerous benefits for skin health:
- Prevention of Sunburns: Sunscreen provides a protective barrier, reducing the risk of sunburn and its associated pain and discomfort.
- Reduction of Premature Aging: By minimizing UV damage, sunscreen helps preserve collagen and elastin, delaying the appearance of wrinkles, fine lines, and sagging skin.
- Lower Risk of Skin Cancer: Sunscreen use significantly reduces the risk of developing skin cancer, including melanoma, by protecting against UV radiation’s DNA-damaging effects.
- Protection Against Hyperpigmentation: Sunscreen minimizes melanin production, helping prevent the formation of dark spots, freckles, and uneven skin tone.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns About Sunscreen Use
Q: Is sunscreen necessary even on cloudy days?
A: Yes, UV radiation can penetrate clouds, so sunscreen is essential even on cloudy days.
Q: Does sunscreen expire?
A: Yes, sunscreen has a shelf life. Check the expiration date on the bottle and discard any expired sunscreen.
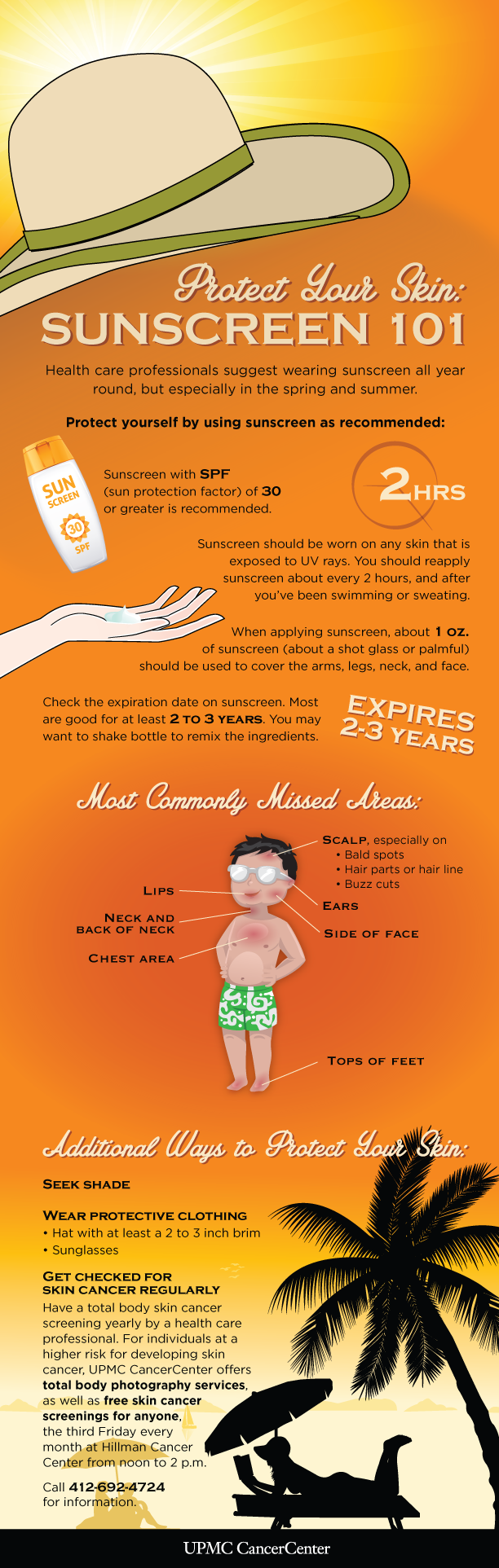
Q: How much sunscreen should I apply?
A: Apply a generous layer of sunscreen to all exposed skin, ensuring complete coverage. A good rule of thumb is to use about a shot glass full of sunscreen for the entire body.
Q: How often should I reapply sunscreen?
A: Reapply sunscreen every two hours, especially after swimming, sweating, or towel drying.
Q: Is sunscreen safe for children?
A: Yes, sunscreen is safe for children, but it’s crucial to use a product specifically formulated for their sensitive skin.
Q: Can sunscreen cause skin irritation or allergies?
A: Some individuals may experience skin irritation or allergies to certain sunscreen ingredients. If you experience any adverse reactions, discontinue use and consult a dermatologist.
Tips for Effective Sunscreen Use
- Choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
- Apply sunscreen liberally and evenly to all exposed skin 20 minutes before sun exposure.
- Reapply sunscreen every two hours, especially after swimming, sweating, or towel drying.
- Wear protective clothing, such as hats, sunglasses, and long sleeves, to further minimize sun exposure.
- Seek shade during peak sun hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.).
- Check the expiration date on your sunscreen and discard any expired products.
- Consult a dermatologist if you have any concerns about sunscreen use or skin conditions.
Conclusion: A Sun-Safe Lifestyle for a Healthier Future
In a world where the sun’s allure often overshadows its potential dangers, understanding the importance of sunscreen is paramount. Sunscreen is not just a cosmetic product; it’s a vital tool for safeguarding skin health, preventing sunburns, and minimizing the risk of skin cancer. By embracing sunscreen as a fundamental part of our sun-safe lifestyle, we can protect our skin from the sun’s harmful rays and enjoy the benefits of a healthy and radiant complexion for years to come.




![[Sun care] Why sunscreen is important! : r/SkincareAddiction](https://i.redd.it/vhroulf0fhi31.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Sun’s Embrace: A Guide to Understanding Sunscreen and its Crucial Role in Skin Health. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
