The Role of Vitamin D in Skin Health: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: The Role of Vitamin D in Skin Health: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Role of Vitamin D in Skin Health: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Role of Vitamin D in Skin Health: A Comprehensive Guide
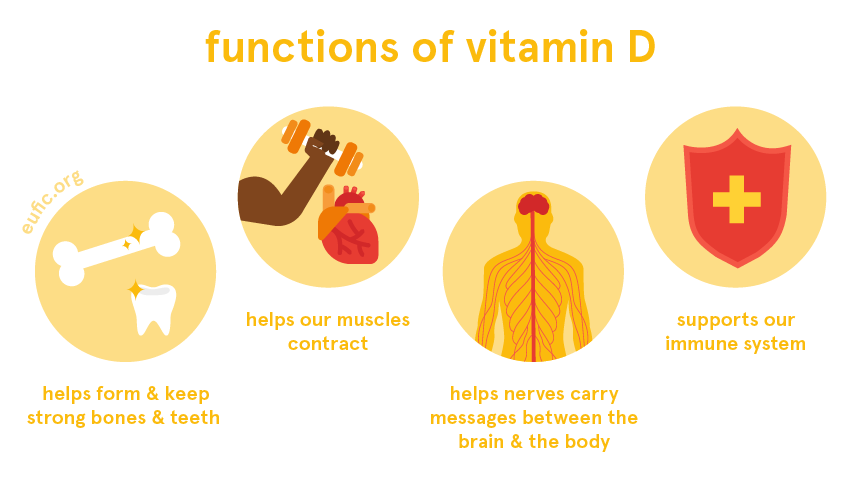
Vitamin D, often referred to as the "sunshine vitamin," plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health, including skin health. While its primary function is to regulate calcium absorption for strong bones, recent research has shed light on its multifaceted impact on skin health, highlighting its potential to protect against various skin conditions and promote a healthy complexion.
Understanding Vitamin D and its Production
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that the body produces naturally when exposed to sunlight. Specifically, ultraviolet B (UVB) rays from the sun trigger the skin to produce vitamin D3, also known as cholecalciferol. This precursor then travels to the liver and kidneys, where it undergoes conversion into its active form, calcitriol.
Beyond sunlight exposure, vitamin D can also be obtained through dietary sources like fatty fish, eggs, and fortified foods. However, many individuals may not get enough vitamin D from these sources alone.
Vitamin D’s Impact on Skin Health
The beneficial effects of vitamin D on skin health are multifaceted, encompassing:
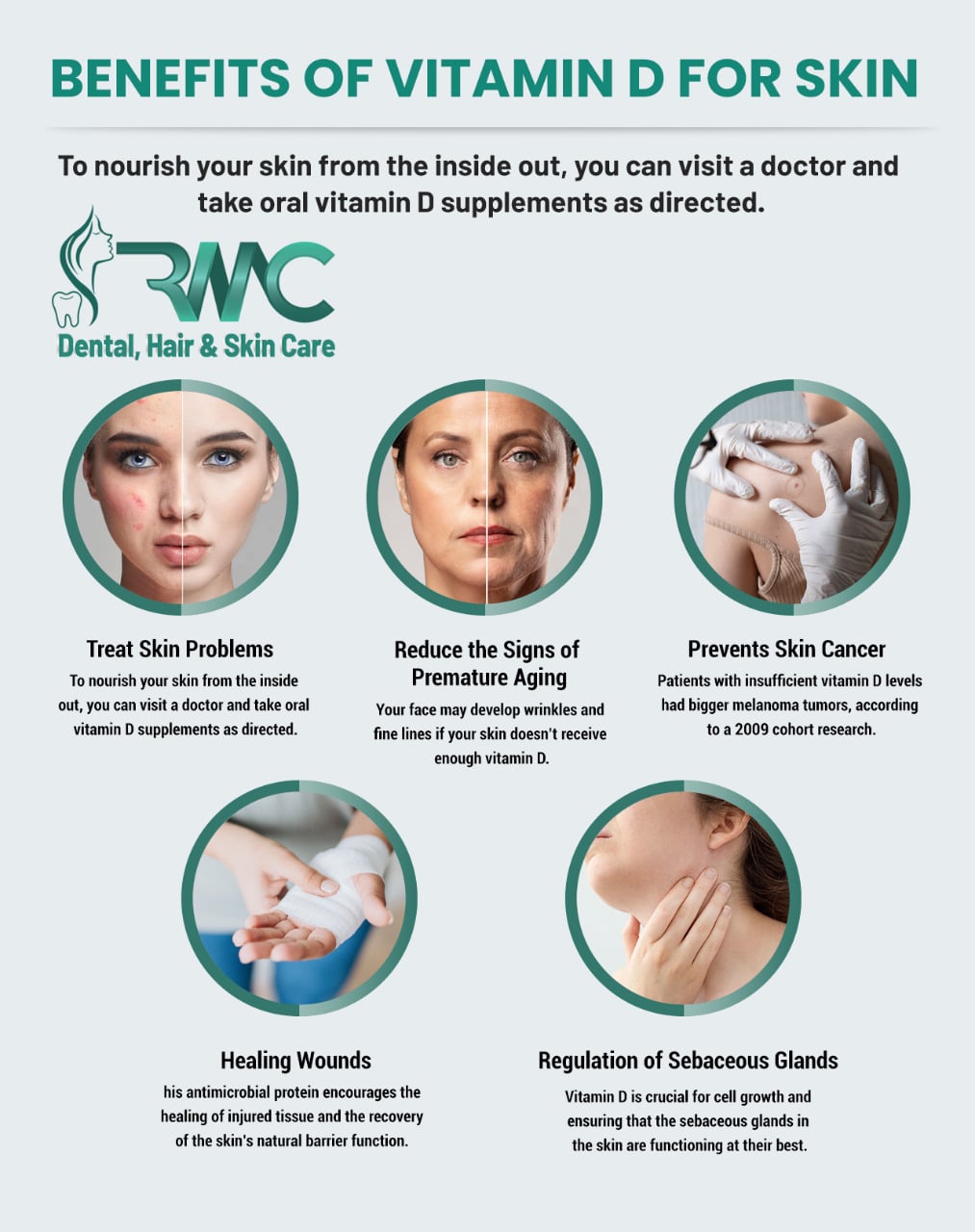
1. Protection Against Skin Cancer:
Emerging research suggests that adequate vitamin D levels may offer protection against certain types of skin cancer. Studies have shown an inverse relationship between vitamin D levels and the risk of melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer. This protective effect may be attributed to vitamin D’s ability to regulate cell growth and differentiation, hindering the development of cancerous cells.
2. Wound Healing and Skin Repair:
Vitamin D plays a vital role in wound healing and skin repair. It stimulates the production of collagen, a protein essential for skin structure and elasticity. Additionally, vitamin D promotes the growth and differentiation of keratinocytes, the primary cells in the epidermis, the outermost layer of skin. This enhanced cell turnover contributes to faster wound healing and improved skin regeneration.
3. Anti-Inflammatory Properties:
Vitamin D exhibits anti-inflammatory properties, which can be beneficial for various skin conditions. It can help reduce inflammation associated with conditions like psoriasis, eczema, and acne. By modulating the immune response and reducing inflammation, vitamin D contributes to improved skin clarity and reduced redness.
4. Acne Management:
While more research is needed, some studies suggest that vitamin D may play a role in acne management. Vitamin D may regulate sebum production, the oily substance that can contribute to acne breakouts. Additionally, its anti-inflammatory properties can help reduce the redness and inflammation associated with acne lesions.
5. Anti-Aging Effects:
Vitamin D’s role in collagen production and skin cell regeneration suggests its potential to combat signs of aging. By promoting collagen synthesis, vitamin D helps maintain skin elasticity and reduce wrinkles. Additionally, its antioxidant properties protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals, which contribute to premature aging.
6. Skin Barrier Function:
Vitamin D is crucial for maintaining a healthy skin barrier, the outermost layer of the skin that protects against environmental aggressors. It helps regulate the production of keratin, a protein that forms the protective barrier. A healthy skin barrier effectively prevents moisture loss, reduces irritation, and protects against infections.
Vitamin D Deficiency and Skin Concerns
A deficiency in vitamin D can lead to various skin concerns, including:
- Psoriasis: A chronic skin condition characterized by scaly, itchy patches, may be exacerbated by vitamin D deficiency.
- Eczema: A condition that causes dry, itchy, and inflamed skin, may be more severe in individuals with low vitamin D levels.
- Acne: Vitamin D deficiency may contribute to increased sebum production, potentially exacerbating acne breakouts.
- Slow Wound Healing: Vitamin D plays a critical role in wound healing, and deficiency can lead to delayed healing and increased risk of infections.
- Skin Infections: A weakened skin barrier due to vitamin D deficiency can increase susceptibility to skin infections.
Factors Affecting Vitamin D Levels
Several factors can influence vitamin D levels, including:
- Age: Vitamin D production declines with age.
- Skin Pigmentation: Darker skin produces less vitamin D from sunlight exposure.
- Geographic Location: Individuals living in regions with less sunlight exposure are more likely to be deficient.
- Lifestyle: Spending time indoors, wearing protective clothing, and using sunscreen can reduce vitamin D production.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as celiac disease and Crohn’s disease, can interfere with vitamin D absorption.
- Medications: Some medications, such as anticonvulsants and corticosteroids, can interfere with vitamin D metabolism.
Determining Vitamin D Levels
If you are concerned about your vitamin D levels, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional. They can order a blood test to determine your vitamin D levels and recommend appropriate treatment if necessary.
Optimizing Vitamin D Levels for Skin Health
To maintain adequate vitamin D levels and support skin health, consider the following strategies:
- Sunlight Exposure: Aim for 10-15 minutes of safe sunlight exposure on most days of the week. Remember to protect your skin from sunburn by using sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
- Dietary Intake: Incorporate vitamin D-rich foods into your diet, such as fatty fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel), eggs, and fortified foods.
- Supplementation: If your diet and sunlight exposure are insufficient, consider supplementing with vitamin D3. The recommended daily intake for adults is 600 IU (international units), but your doctor can determine the appropriate dosage based on your individual needs.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Reduce time spent indoors, wear less protective clothing, and consider moving to a sunnier climate if possible.
FAQs about Vitamin D Skin Care
1. How much sunlight exposure is safe for vitamin D production?
The recommended amount of sunlight exposure for vitamin D production varies depending on factors such as skin pigmentation, geographic location, and time of year. Generally, 10-15 minutes of safe sunlight exposure on most days of the week is sufficient for most individuals. However, it is crucial to protect your skin from sunburn by using sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
2. Can I get enough vitamin D from diet alone?
While some foods are good sources of vitamin D, it can be challenging to obtain sufficient amounts from diet alone. Many individuals may need to supplement with vitamin D3 to reach optimal levels.
3. Is it safe to take vitamin D supplements?
Vitamin D supplements are generally safe when taken at recommended dosages. However, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional before starting any supplements, as excessive intake can lead to toxicity.
4. How long does it take for vitamin D levels to increase with supplementation?
It typically takes 4-6 weeks for vitamin D levels to increase with supplementation.
5. Can I use vitamin D oil topically for skin care?
Topical vitamin D products are available, but their effectiveness for skin health is not fully established. More research is needed to determine the optimal dosage and formulation for topical application.
Tips for Vitamin D Skin Care
- Monitor your vitamin D levels: Consult a healthcare professional to get your vitamin D levels checked and discuss supplementation options if needed.
- Maximize safe sun exposure: Aim for 10-15 minutes of safe sunlight exposure on most days of the week, but remember to protect your skin from sunburn with sunscreen.
- Incorporate vitamin D-rich foods into your diet: Include fatty fish, eggs, and fortified foods in your meals.
- Consider supplementation: If your diet and sunlight exposure are insufficient, discuss supplementation with your doctor.
- Use sunscreen regularly: Protect your skin from harmful UV rays by applying sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher daily.
Conclusion
Vitamin D plays a vital role in maintaining skin health, contributing to protection against skin cancer, wound healing, anti-inflammatory effects, acne management, anti-aging benefits, and a healthy skin barrier. By optimizing your vitamin D levels through sunlight exposure, dietary intake, and supplementation, you can support overall skin health and promote a radiant complexion. However, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional to determine your individual needs and ensure safe and effective vitamin D management.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Role of Vitamin D in Skin Health: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
