The Power of Visual Representation: Unpacking the Essence of Product Mockups
Related Articles: The Power of Visual Representation: Unpacking the Essence of Product Mockups
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Power of Visual Representation: Unpacking the Essence of Product Mockups. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Visual Representation: Unpacking the Essence of Product Mockups
In the realm of design and development, effective communication is paramount. This is especially true when translating abstract ideas into tangible products. Enter the product mockup: a powerful tool that bridges the gap between imagination and reality, enabling stakeholders to visualize and evaluate design concepts before committing to costly production.
Defining the Concept:
A product mockup is a visual representation of a product, typically created in a digital format. It serves as a blueprint, showcasing the product’s design, functionality, and overall user experience. Mockups can range from simple sketches and wireframes to highly detailed, interactive prototypes. The level of detail and sophistication employed depends on the project’s scope and the intended audience.
Unveiling the Benefits:
The use of product mockups extends beyond mere aesthetics. They offer a multitude of benefits, streamlining the design process and fostering effective collaboration:
1. Communicating Ideas with Clarity:
Mockups act as a universal language, facilitating clear communication between designers, developers, and stakeholders. They provide a shared visual reference point, minimizing ambiguity and ensuring everyone is on the same page regarding the product’s intended form and function.
2. Early Stage Feedback and Iteration:
Mockups offer an invaluable opportunity to gather feedback at the early stages of product development. By presenting a visual representation, designers can receive constructive criticism and suggestions for improvement before investing significant time and resources in actual development. This iterative process ensures that the final product aligns with user needs and market expectations.
3. Testing User Experience and Usability:
Mockups allow for early testing of the user experience (UX) and usability of a product. By simulating user interactions, designers can identify potential pain points and areas for improvement. This iterative process ensures that the final product is intuitive, user-friendly, and meets the needs of its target audience.
4. Validating Design Concepts:
Mockups provide a tangible representation of design concepts, enabling stakeholders to assess their feasibility and appeal. By visualizing the product in its intended context, stakeholders can evaluate its aesthetics, functionality, and overall brand identity. This early validation helps to minimize costly revisions and ensure that the product aligns with the brand’s vision.
5. Exploring Different Design Variations:
Mockups facilitate the exploration of multiple design variations, allowing designers to compare and contrast different approaches. This process enables informed decision-making, ensuring that the final design is the most effective and appealing option.
6. Enhancing User Engagement and Excitement:
Mockups can be used to generate excitement and anticipation for upcoming products. By showcasing a visual representation of the product, companies can engage their target audience and create a buzz around the launch.
Types of Product Mockups:
The realm of product mockups encompasses a diverse range of formats, each suited to specific purposes and audiences:
1. Wireframes:
These skeletal representations focus on the product’s layout, structure, and basic functionality. They are often used in the early stages of design to establish the product’s core elements and user flow.
2. Low-Fidelity Mockups:
These mockups provide a more detailed representation of the product’s design, incorporating basic visual elements and interactive features. They are typically created using tools like Balsamiq or Sketch.
3. High-Fidelity Mockups:
These mockups closely resemble the final product, incorporating realistic visuals, interactive elements, and detailed functionality. They are often created using design tools like Adobe XD or Figma.
4. Prototypes:
These interactive mockups allow users to experience the product’s functionality and flow. They are typically created using prototyping tools like InVision or Proto.io.
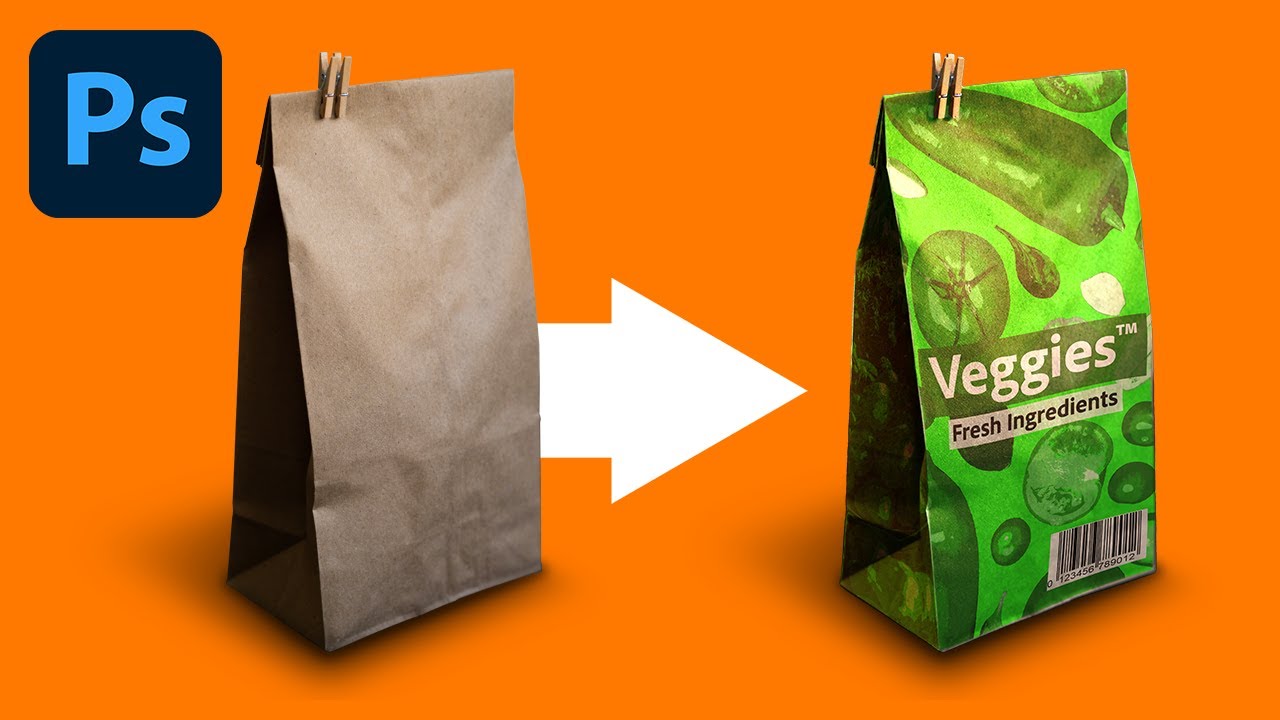
5. 3D Mockups:
These realistic representations showcase the product’s three-dimensional form and texture. They are often used for products with complex geometries or intricate details.
Creating Effective Product Mockups:
To ensure that product mockups effectively communicate their intended message, several key considerations must be kept in mind:
1. Define the Target Audience:
The level of detail and complexity of a mockup should be tailored to the intended audience. For instance, a mockup presented to investors may require more detailed information than one shared with internal stakeholders.
2. Focus on Clarity and Simplicity:
Mockups should be visually appealing and easy to understand. Avoid overwhelming the audience with too much information or intricate details.
3. Utilize High-Quality Visuals:
High-resolution images and realistic representations enhance the impact and credibility of mockups.
4. Incorporate Interactivity:
Interactive mockups allow users to experience the product’s functionality and engage with its features.
5. Seek Feedback and Iterate:
Continuously gather feedback from stakeholders and iterate on the mockup based on the insights gained.
FAQs: Demystifying the Product Mockup
Q: What is the difference between a mockup and a prototype?
A: While both mockups and prototypes are visual representations of a product, they differ in their level of interactivity. Mockups are static representations that showcase the product’s design and functionality, while prototypes are interactive representations that allow users to experience the product’s flow and features.
Q: When should I use a product mockup?
A: Product mockups are valuable throughout the design and development process. They can be used to:
- Communicate design concepts to stakeholders
- Gather feedback and iterate on designs
- Test user experience and usability
- Validate design concepts
- Generate excitement for upcoming products
Q: What are some popular tools for creating product mockups?
A: There are numerous tools available for creating product mockups, ranging from simple sketching software to sophisticated prototyping platforms. Some popular options include:
- Adobe XD
- Figma
- Sketch
- Balsamiq
- InVision
- Proto.io
Tips for Creating Effective Product Mockups:
- Start with a clear goal: What do you want to achieve with the mockup?
- Keep it simple and focused: Avoid overwhelming the audience with too much information.
- Use high-quality visuals: Invest in professional-looking imagery or illustrations.
- Incorporate interactivity: Allow users to interact with the mockup to experience its functionality.
- Seek feedback and iterate: Gather feedback from stakeholders and refine the mockup based on their insights.
Conclusion:
Product mockups are an indispensable tool for effective communication and collaboration in the design and development process. They bridge the gap between imagination and reality, enabling stakeholders to visualize and evaluate design concepts before committing to costly production. By leveraging the power of visual representation, product mockups facilitate clear communication, enable early feedback and iteration, and ultimately contribute to the creation of successful and user-centric products.


![What Is Product Marketing? [Strategy, KPIs , Examples]](https://www.tidio.com/wp-content/uploads/visual-representation-of-product-marketing-1200x977.png)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Visual Representation: Unpacking the Essence of Product Mockups. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
