The Complexities of Acne: Understanding the Contributing Factors
Related Articles: The Complexities of Acne: Understanding the Contributing Factors
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Complexities of Acne: Understanding the Contributing Factors. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Complexities of Acne: Understanding the Contributing Factors
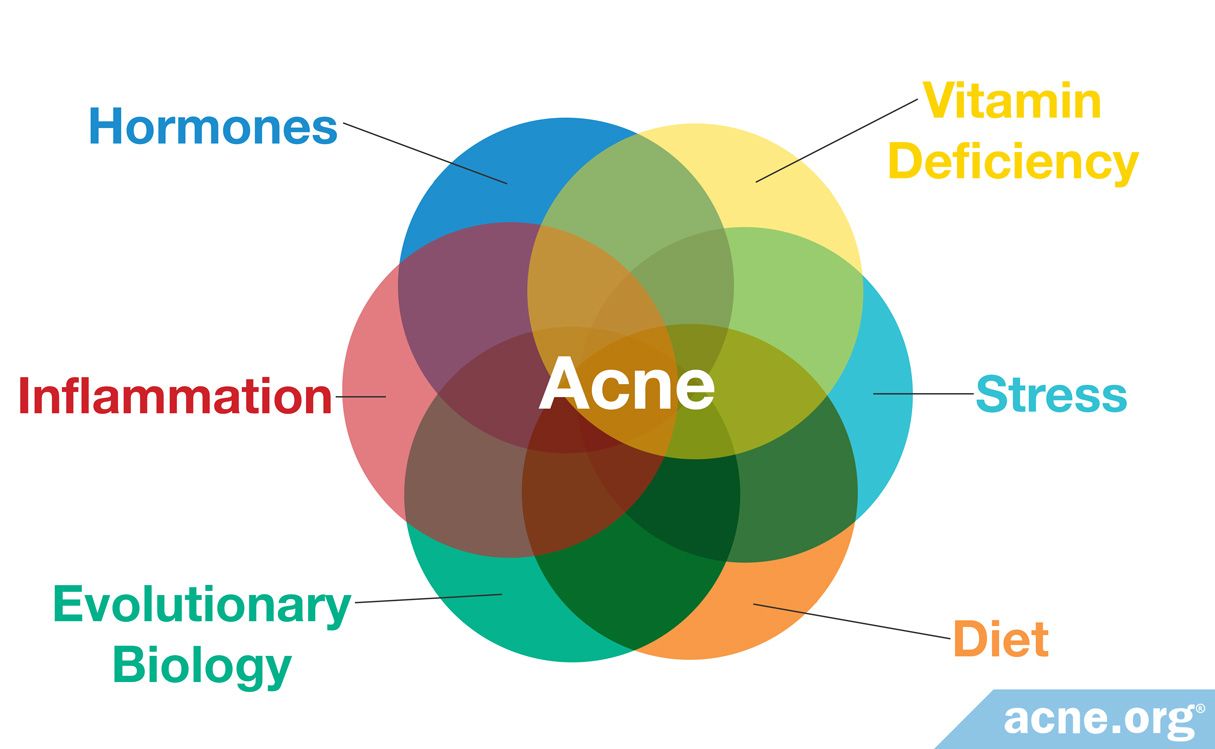
Acne, a common skin condition affecting individuals of all ages, is characterized by the appearance of pimples, whiteheads, blackheads, and sometimes, cysts. While often perceived as a purely cosmetic concern, acne can significantly impact self-esteem and mental well-being. Understanding the contributing factors to acne is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies and managing this condition.
The Role of Hormones:
Hormonal fluctuations play a pivotal role in acne development, particularly during puberty, menstruation, and pregnancy. The surge in androgens, specifically testosterone, stimulates sebaceous gland activity, leading to increased sebum production. This excess oil can clog hair follicles, creating a breeding ground for Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes), a bacterium commonly found on the skin.
The Influence of Genetics:
Genetic predisposition is a significant factor in acne susceptibility. Studies have identified specific genes associated with increased sebum production, altered follicular keratinization, and inflammation. Family history of acne, therefore, increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
The Impact of Diet:
While not a direct cause, certain dietary choices can exacerbate acne symptoms. High glycemic index (GI) foods, such as sugary drinks and refined carbohydrates, trigger an inflammatory response, potentially contributing to acne flare-ups. Dairy products, particularly skim milk, have also been linked to increased acne severity in some individuals.
The Role of Stress:
Stress can trigger hormonal changes that contribute to acne. Elevated cortisol levels, the body’s stress hormone, can stimulate sebum production and inflammation. Chronic stress can also disrupt sleep patterns, further impacting skin health and acne severity.
The Importance of Skincare Practices:
Improper skincare practices can worsen existing acne and contribute to new breakouts. Over-washing the skin can strip it of its natural oils, leading to dryness and irritation. Harsh scrubbing can also damage the skin barrier, increasing inflammation and susceptibility to acne.
The Impact of Environmental Factors:
Environmental factors, including pollution, humidity, and heat, can also contribute to acne. Pollution particles can clog pores, while humidity and heat can exacerbate sebum production. Exposure to sunlight, particularly ultraviolet (UV) radiation, can also trigger inflammation and worsen acne symptoms.
The Role of Medications:
Certain medications, including corticosteroids, lithium, and androgenic hormones, can induce or worsen acne. These medications can alter hormonal balance or directly stimulate sebum production, contributing to acne development.
The Impact of Underlying Medical Conditions:
Some medical conditions, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can be associated with acne. PCOS, a hormonal disorder, often leads to increased androgen levels, contributing to sebum production and acne.
Understanding the Mechanisms:
The development of acne involves a complex interplay of factors, culminating in the formation of lesions. The process typically begins with the overproduction of sebum, a waxy substance secreted by the sebaceous glands. This excess sebum, along with dead skin cells, can clog the hair follicles, creating a blockage known as a comedo.
Comedones can be either open (blackheads) or closed (whiteheads). Open comedones appear black due to oxidation of the sebum, while closed comedones are covered by a thin layer of skin. These comedones can become inflamed when bacteria, particularly P. acnes, colonize the trapped sebum. This bacterial proliferation triggers an inflammatory response, leading to the formation of papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts.
Addressing Acne: A Multifaceted Approach
Treating acne requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the underlying contributing factors. Topical medications, such as benzoyl peroxide and retinoids, can help reduce inflammation and unclog pores. Oral medications, such as antibiotics and hormonal therapies, may also be prescribed to combat bacterial infection and regulate hormone levels.
Lifestyle modifications, including stress management, regular exercise, and a balanced diet, can complement medical treatments. Maintaining a consistent skincare routine, using non-comedogenic products, and avoiding harsh scrubbing are crucial for preventing further irritation and breakouts.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can acne be cured?
A: While there is no cure for acne, it is a manageable condition. With appropriate treatment and lifestyle modifications, individuals can achieve significant improvement in their acne symptoms.
Q: Does stress cause acne?
A: Stress can trigger hormonal changes that contribute to acne flare-ups. Elevated cortisol levels can stimulate sebum production and inflammation, exacerbating existing acne.
Q: Can diet affect acne?
A: While diet alone does not cause acne, certain dietary choices can worsen symptoms. High-glycemic index foods and dairy products have been linked to increased acne severity in some individuals.
Q: Is acne contagious?
A: Acne is not contagious. It is caused by a combination of factors, including hormonal fluctuations, genetics, and bacteria.
Q: What are the best ways to prevent acne?
A: Preventing acne involves a combination of strategies, including:
- Maintaining a consistent skincare routine with gentle cleansers and non-comedogenic products.
- Avoiding harsh scrubbing and over-washing the skin.
- Managing stress through techniques like exercise, meditation, or yoga.
- Following a balanced diet and limiting consumption of high-glycemic index foods and dairy products.
Tips for Managing Acne
- Consult a dermatologist: Seeking professional advice from a dermatologist is essential for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans.
- Follow a consistent skincare routine: Cleanse your skin twice daily with a gentle cleanser, apply a moisturizer, and consider using a topical acne treatment as prescribed by your dermatologist.
- Avoid picking or squeezing pimples: This can worsen inflammation and increase the risk of scarring.
- Wear sunscreen daily: Protecting your skin from UV radiation can help prevent further inflammation and hyperpigmentation.
- Manage stress levels: Engage in stress-reducing activities like exercise, meditation, or yoga to minimize hormonal fluctuations.
- Eat a balanced diet: Limit consumption of sugary drinks, refined carbohydrates, and dairy products, which can contribute to acne flare-ups.
Conclusion
Acne is a common skin condition with a complex etiology, influenced by a multitude of factors. While hormonal fluctuations, genetics, and dietary choices play significant roles, environmental factors, skincare practices, and underlying medical conditions can also contribute to its development. Understanding the intricate mechanisms behind acne is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies and managing this condition. A multifaceted approach that addresses the underlying contributing factors, including medical treatments, lifestyle modifications, and appropriate skincare practices, is essential for achieving optimal results.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Complexities of Acne: Understanding the Contributing Factors. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
