Delving into the Realm of Viscosity: Understanding the Concept of Specific Viscosity
Related Articles: Delving into the Realm of Viscosity: Understanding the Concept of Specific Viscosity
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Delving into the Realm of Viscosity: Understanding the Concept of Specific Viscosity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Delving into the Realm of Viscosity: Understanding the Concept of Specific Viscosity

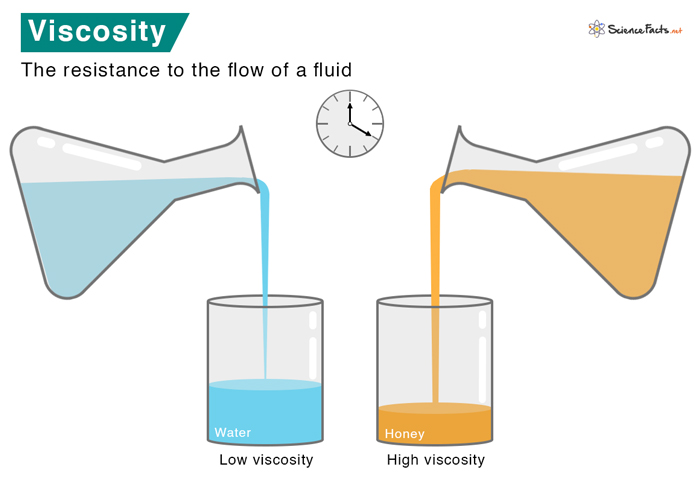
Viscosity, a fundamental property of fluids, describes their resistance to flow. While it’s a familiar concept in everyday life – think of honey flowing slowly compared to water – its precise measurement and interpretation become crucial in scientific and industrial contexts. One important aspect of viscosity measurement is the concept of specific viscosity, which provides a valuable tool for understanding the behavior of solutions and suspensions.
Defining Specific Viscosity
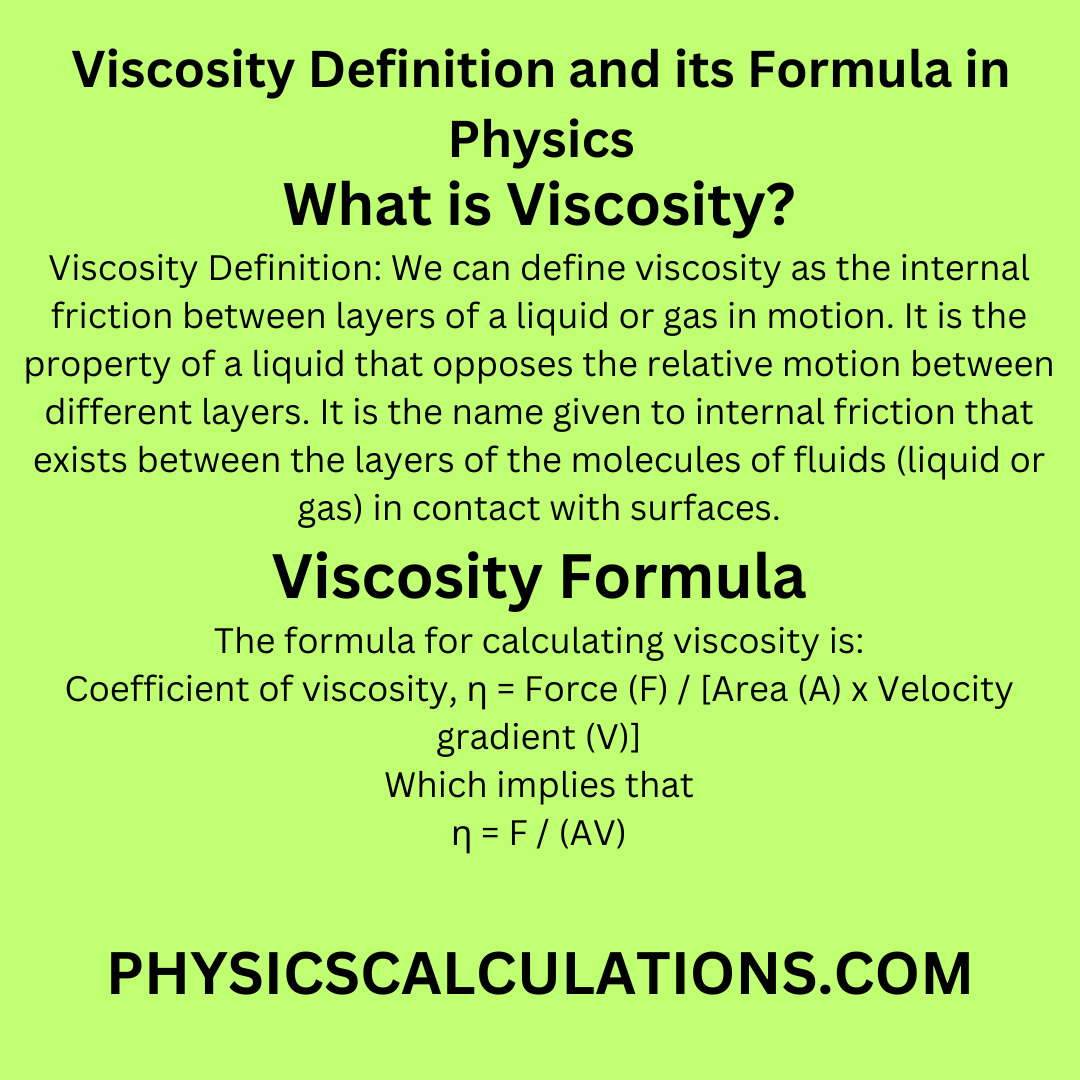
Specific viscosity, denoted by ηsp, is a dimensionless quantity that quantifies the change in viscosity of a solution or suspension relative to its pure solvent. It represents the increase in viscosity caused by the presence of solute particles or dispersed particles.
Mathematically, specific viscosity is defined as:
ηsp = (η – η0) / η0
Where:
- η is the viscosity of the solution or suspension
- η0 is the viscosity of the pure solvent
Interpreting Specific Viscosity
A specific viscosity value of 1 indicates that the solution or suspension has twice the viscosity of the pure solvent. A value of 2 indicates three times the viscosity, and so on. A specific viscosity less than 1 implies that the solution or suspension has a lower viscosity than the pure solvent.
Factors Influencing Specific Viscosity
Specific viscosity is influenced by several factors, including:
- Concentration of the solute or dispersed particles: Higher concentrations generally lead to higher specific viscosities.
- Size and shape of the solute or dispersed particles: Larger or more asymmetric particles tend to increase viscosity more significantly.
- Interactions between solute or dispersed particles: Strong interactions, such as electrostatic attractions or hydrogen bonding, can contribute to higher viscosity.
- Temperature: Viscosity generally decreases with increasing temperature.
Applications of Specific Viscosity
Specific viscosity plays a crucial role in various scientific and industrial fields, including:
- Polymer science: It helps determine the molecular weight and chain entanglement of polymers in solution, providing insights into their physical properties.
- Colloid and surface science: Specific viscosity is used to study the behavior of dispersions and emulsions, aiding in the development of stable formulations.
- Food science: It helps understand the flow properties of food products like sauces, jams, and yogurt, influencing their texture and mouthfeel.
- Pharmaceutical science: Specific viscosity is vital in characterizing the viscosity of drug formulations, ensuring proper drug delivery and bioavailability.
Benefits of Using Specific Viscosity
- Relative comparison: Specific viscosity allows for a direct comparison of the viscosity of different solutions or suspensions relative to their respective solvents.
- Sensitivity to changes: It is highly sensitive to changes in concentration, size, and shape of solute or dispersed particles, making it a valuable tool for monitoring and controlling these parameters.
- Predictive power: Specific viscosity can be used to predict the viscosity of a solution or suspension at different concentrations or under different conditions.
FAQs on Specific Viscosity
1. What is the difference between specific viscosity and intrinsic viscosity?
Specific viscosity is a measure of the relative increase in viscosity due to the presence of solute particles. Intrinsic viscosity, on the other hand, is a measure of the viscosity increase per unit concentration, extrapolated to infinite dilution.
2. Why is specific viscosity dimensionless?
Specific viscosity is dimensionless because it is a ratio of two viscosities, which have the same units (Pa·s or poise).
3. How is specific viscosity measured?
Specific viscosity can be measured using various techniques, including:
- Capillary viscometers: Measure the time it takes for a fixed volume of fluid to flow through a capillary tube.
- Rotational viscometers: Measure the torque required to rotate a spindle immersed in the fluid.
- Vibrational viscometers: Measure the damping of a vibrating element immersed in the fluid.
4. What are the limitations of specific viscosity?
Specific viscosity is primarily applicable to dilute solutions or suspensions. At higher concentrations, interactions between solute or dispersed particles become more complex, making the interpretation of specific viscosity less straightforward.
Tips for Understanding and Using Specific Viscosity
- Ensure accurate solvent viscosity: The accuracy of specific viscosity measurements depends on the precise determination of the solvent viscosity.
- Consider concentration effects: Specific viscosity is highly sensitive to concentration, so it is crucial to use appropriate concentrations for meaningful comparisons.
- Account for temperature effects: Temperature significantly affects viscosity, so ensure consistent temperature control during measurements.
- Interpret data cautiously: Specific viscosity is a relative measure and should be interpreted in conjunction with other relevant parameters.
Conclusion
Specific viscosity provides a valuable tool for understanding the rheological behavior of solutions and suspensions. Its ability to quantify the change in viscosity relative to the pure solvent makes it a powerful tool for characterizing and controlling the properties of various materials in diverse fields. By understanding the factors influencing specific viscosity and interpreting its measurements appropriately, researchers and engineers can gain insights into the complex flow behavior of fluids, ultimately leading to the development of new and improved materials and products.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delving into the Realm of Viscosity: Understanding the Concept of Specific Viscosity. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
