Deciphering the Language of Lubrication: A Comprehensive Guide to Oil Viscosity
Related Articles: Deciphering the Language of Lubrication: A Comprehensive Guide to Oil Viscosity
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Language of Lubrication: A Comprehensive Guide to Oil Viscosity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Deciphering the Language of Lubrication: A Comprehensive Guide to Oil Viscosity
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Deciphering the Language of Lubrication: A Comprehensive Guide to Oil Viscosity
- 3.1 Viscosity: The Flow of Protection
- 3.2 Understanding the Viscosity Rating System: SAE Grades
- 3.3 Factors Influencing Oil Viscosity Selection
- 3.4 Beyond Viscosity: Other Oil Properties
- 3.5 The Importance of Regular Oil Changes
- 3.6 FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of Oil Viscosity
- 3.7 Tips for Choosing the Right Oil Viscosity
- 3.8 Conclusion: The Foundation of Engine Health
- 4 Closure
Deciphering the Language of Lubrication: A Comprehensive Guide to Oil Viscosity
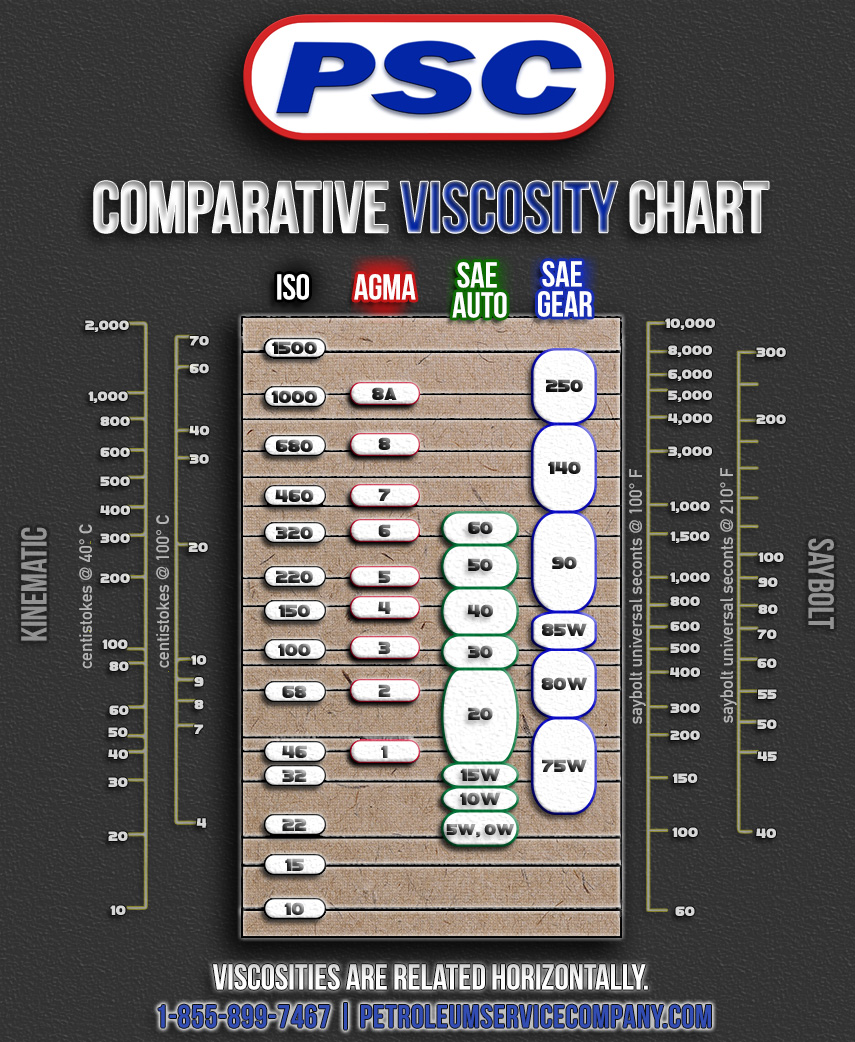
The engine, the heart of any vehicle, relies on a vital fluid for its smooth operation: engine oil. Beyond simply lubricating moving parts, engine oil performs a multitude of crucial tasks, including cooling, cleaning, and protecting against wear and tear. One of the most important characteristics of engine oil is its viscosity, a measure of its resistance to flow. Understanding viscosity is key to selecting the right oil for your vehicle and ensuring optimal engine performance.
Viscosity: The Flow of Protection
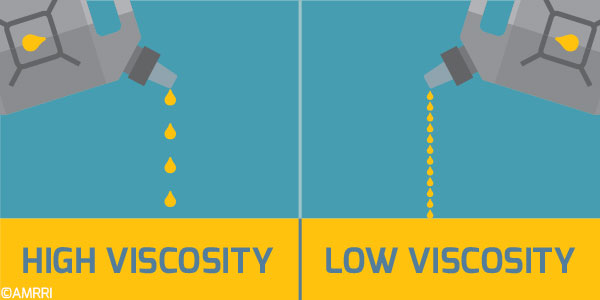
Viscosity is often described as the "thickness" of a fluid. A high viscosity oil is thick and flows slowly, while a low viscosity oil is thin and flows readily. In the context of engine oil, viscosity plays a critical role in determining how effectively it can lubricate engine components.
High viscosity oils excel in high-temperature environments, providing a robust protective film between moving parts. This is particularly beneficial during hot weather or under heavy engine load. However, high viscosity oils can hinder engine start-up, especially in cold temperatures, as they may struggle to reach all moving parts quickly.
Low viscosity oils, on the other hand, flow easily and readily reach all engine components, even in cold conditions. This ensures smooth engine start-up and reduces friction, leading to improved fuel efficiency. However, low viscosity oils may not provide adequate protection at high temperatures or under extreme engine load.
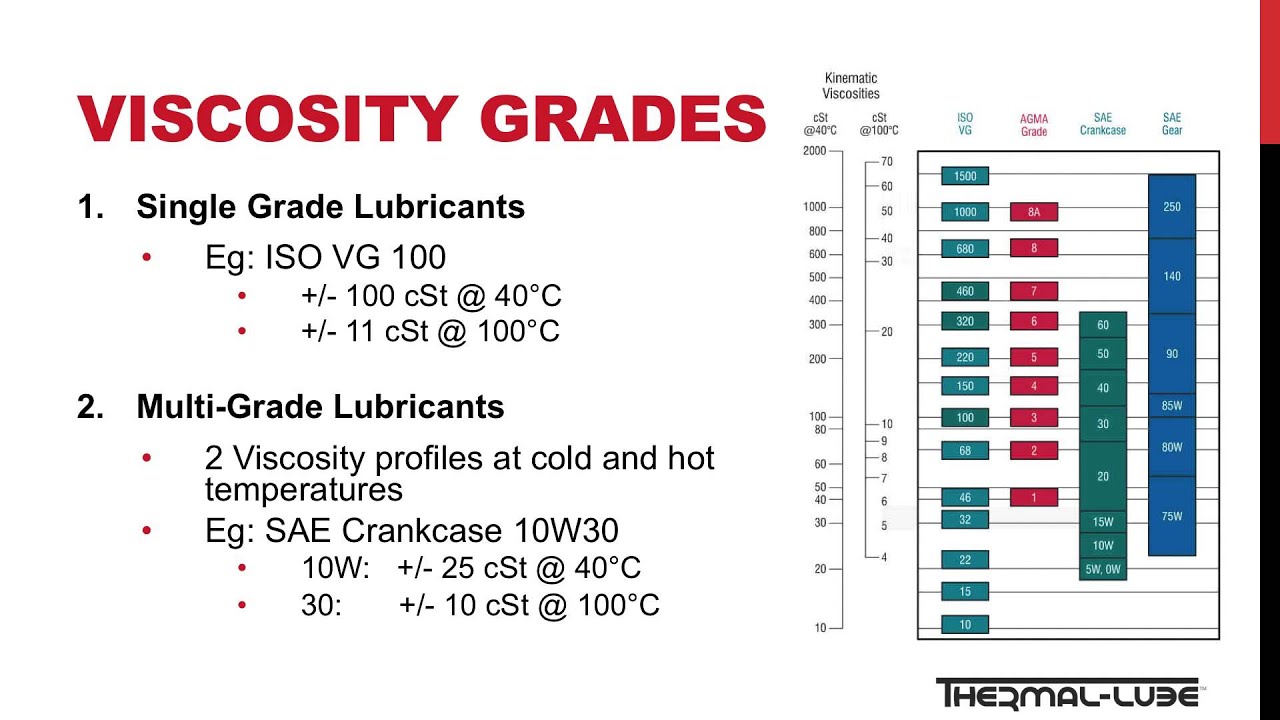
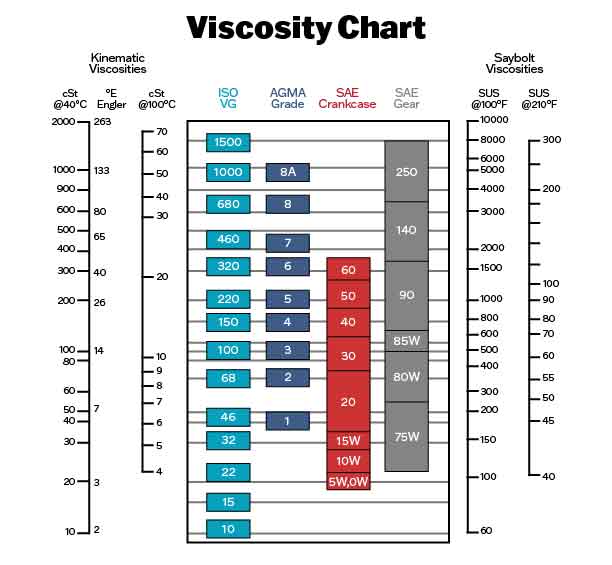
Understanding the Viscosity Rating System: SAE Grades
To standardize oil viscosity, the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) developed a system of viscosity grades, expressed as a numerical value followed by a letter (e.g., SAE 5W-30). The first number represents the oil’s viscosity at low temperatures (Winter), while the second number indicates its viscosity at high temperatures (Summer).
- Winter (W) Grades: Lower numbers indicate thinner oil that flows easily at low temperatures, facilitating cold starts.
- Summer Grades: Higher numbers denote thicker oil that maintains its protective film at high temperatures.
For example, SAE 5W-30 oil is considered a multi-grade oil, meaning it can operate effectively in a wide range of temperatures. The "5W" indicates that the oil is suitable for temperatures as low as -25°C, while the "30" signifies its ability to maintain its viscosity at high temperatures.
Factors Influencing Oil Viscosity Selection
Choosing the right oil viscosity for your vehicle depends on several factors:
- Engine Type: Different engines have varying tolerances for oil viscosity. Modern engines with tighter tolerances may require thinner oils, while older engines with looser tolerances may benefit from thicker oils.
- Climate: The temperature range where the vehicle operates is crucial. In cold climates, thinner oils are preferred for easier cold starts, while thicker oils are recommended in hot climates for better protection at high temperatures.
- Driving Conditions: Frequent heavy loads or extreme driving conditions necessitate thicker oils for enhanced protection.
- Vehicle Manufacturer Recommendations: Consult your owner’s manual for the specific viscosity grade recommended by the vehicle manufacturer. This information is crucial for optimal engine performance and longevity.
Beyond Viscosity: Other Oil Properties
While viscosity is a key factor in oil selection, other properties also play a crucial role in ensuring proper engine lubrication:
- Additives: Modern engine oils contain various additives that enhance their performance, such as detergents to keep the engine clean, anti-wear agents to reduce friction, and antioxidants to prevent oil degradation.
- API Service Classification: The American Petroleum Institute (API) classifies engine oils based on their performance characteristics, such as their ability to protect against wear, deposits, and oxidation.
The Importance of Regular Oil Changes
Oil viscosity degrades over time due to heat, oxidation, and contamination. Regular oil changes are essential to maintain optimal engine performance and ensure proper lubrication. The frequency of oil changes depends on factors such as driving conditions, oil type, and vehicle manufacturer recommendations.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of Oil Viscosity
Q: Can I use a different viscosity oil than what is recommended in my owner’s manual?
A: It is generally not recommended to deviate from the manufacturer’s recommendations. Using an oil with a different viscosity may affect engine performance, fuel economy, and overall engine health.
Q: What happens if I use an oil that is too thick or too thin?
A: Using an oil that is too thick can lead to increased friction, reduced fuel efficiency, and difficulty starting the engine in cold temperatures. Conversely, using an oil that is too thin may not provide adequate protection at high temperatures or under heavy engine load, leading to increased wear and tear.
Q: How often should I change my engine oil?
A: The frequency of oil changes depends on factors such as driving conditions, oil type, and vehicle manufacturer recommendations. Refer to your owner’s manual for specific guidelines.
Q: Can I use synthetic oil instead of conventional oil?
A: Synthetic oils offer several advantages over conventional oils, including improved performance, longer life, and better protection at extreme temperatures. However, they are typically more expensive. Consult your owner’s manual to determine if synthetic oil is recommended for your vehicle.
Tips for Choosing the Right Oil Viscosity
- Consult your owner’s manual: This is the most reliable source for the recommended oil viscosity for your vehicle.
- Consider your driving conditions: If you frequently drive in extreme temperatures or under heavy loads, you may need to use a thicker oil.
- Consult a qualified mechanic: A mechanic can help you choose the right oil viscosity for your vehicle based on your specific needs and driving conditions.
Conclusion: The Foundation of Engine Health
Choosing the right oil viscosity is crucial for maintaining optimal engine performance, fuel efficiency, and longevity. By understanding the factors influencing oil viscosity selection and following the recommendations of your vehicle manufacturer, you can ensure your engine receives the proper lubrication it needs to operate smoothly and reliably. Remember, regular oil changes are essential to maintain the effectiveness of your engine oil and ensure optimal engine health.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Language of Lubrication: A Comprehensive Guide to Oil Viscosity. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
