A Comprehensive Guide to Wound Care Products: Types, Applications, and Importance
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Wound Care Products: Types, Applications, and Importance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Wound Care Products: Types, Applications, and Importance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Wound Care Products: Types, Applications, and Importance

Wound care is an essential aspect of healthcare, encompassing a wide range of products and practices designed to promote healing and prevent complications. From simple cuts and scrapes to complex surgical wounds, the appropriate use of wound care products is crucial for optimal patient outcomes. This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse types of wound care products available, highlighting their specific applications, benefits, and considerations.
1. Wound Cleansers:
Wound cleansers are the first line of defense in wound care, effectively removing debris, bacteria, and contaminants that can impede healing. Their primary function is to create a clean and sterile environment for the wound to begin the healing process.
Types of Wound Cleansers:
- Antiseptic Solutions: These solutions, often containing iodine, chlorhexidine, or hydrogen peroxide, possess antimicrobial properties that kill bacteria and reduce the risk of infection.
- Sterile Saline Solution: This is a gentle, non-irritating solution that effectively removes debris without harming the wound. It is particularly suitable for sensitive wounds and those requiring minimal disruption.
- Wound Irrigation Solutions: These solutions are designed for flushing wounds with high pressure, effectively removing embedded debris and foreign objects.
Benefits of Wound Cleansers:
- Reduced Infection Risk: By eliminating bacteria and other contaminants, wound cleansers significantly reduce the risk of infection, a major concern in wound healing.
- Improved Healing Environment: A clean wound allows for optimal tissue regeneration and reduces the likelihood of scar formation.
- Pain Management: Gentle cleansing can minimize pain and discomfort associated with the wound.
Considerations:
- Type of Wound: The choice of cleanser depends on the type of wound, its location, and the presence of any specific contaminants.
- Sensitivity: Certain cleansers can be irritating to sensitive skin, requiring careful selection based on individual tolerance.
- Frequency: The frequency of cleansing depends on the wound’s characteristics and the type of cleanser used.
FAQs:
- Q: Can I use soap to clean a wound?
- A: While soap can be used to cleanse surrounding skin, it is not recommended for direct wound cleaning due to potential irritation and interference with healing.
- Q: What should I do if a wound is contaminated with dirt or debris?
- A: Irrigate the wound thoroughly with sterile saline solution or a designated wound irrigation solution to remove all contaminants.
Tips:
- Always cleanse wounds gently to avoid further damage.
- Use sterile materials and techniques to prevent introducing new contaminants.
- Consult a healthcare professional for guidance on wound care and the appropriate cleanser for specific wounds.
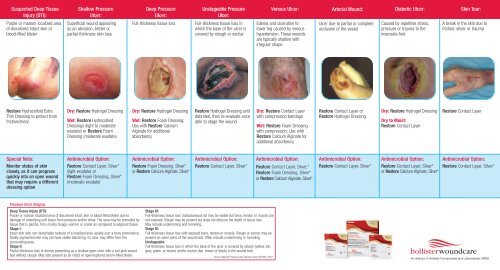
2. Wound Dressings:
Wound dressings serve as a protective barrier over the wound, promoting healing and preventing infection. They come in various forms, each designed for specific wound types and stages of healing.
Types of Wound Dressings:
- Gauze Dressings: These are the most common type, providing a basic barrier and absorbing excess exudate. They are available in various sizes and thicknesses, allowing for customization based on wound size and exudate levels.
- Hydrocolloid Dressings: These dressings create a moist environment that promotes wound healing and protects against bacterial contamination. They are often used for partial-thickness wounds and pressure ulcers.
- Foam Dressings: Designed to absorb large amounts of exudate, foam dressings are particularly effective for wounds with high drainage. They also provide cushioning and support.
- Alginate Dressings: Made from seaweed extracts, alginate dressings are highly absorbent and form a gel that helps maintain a moist environment. They are often used for wounds with heavy exudate and can be packed into deep cavities.
- Transparent Film Dressings: These thin, transparent dressings allow for easy visualization of the wound while providing a barrier against bacteria and moisture. They are often used for superficial wounds, burns, and skin grafts.
Benefits of Wound Dressings:
- Protection from Infection: Dressings act as a barrier against bacteria and other contaminants, preventing infection and promoting healing.
- Exudate Management: Dressings absorb excess wound exudate, keeping the wound clean and dry.
- Moisture Control: Different dressings create different levels of moisture, allowing for optimal healing conditions.
- Pain Reduction: Dressings can provide cushioning and support, reducing pain and discomfort.
Considerations:
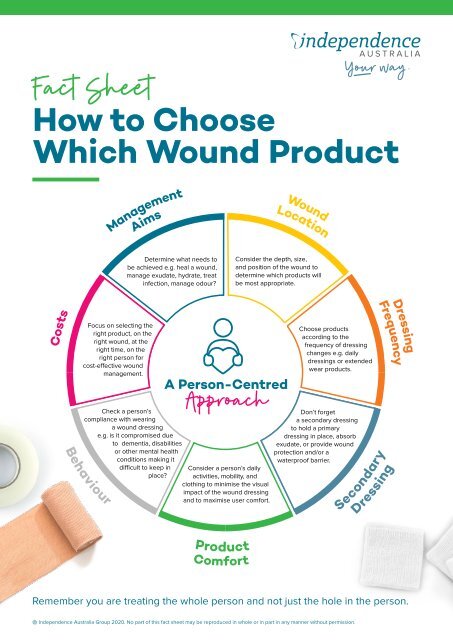
- Type of Wound: The choice of dressing depends on the wound type, size, and stage of healing.
- Exudate Level: Dressings should be selected based on the amount of exudate produced by the wound.
- Frequency of Change: The frequency of dressing changes varies depending on the type of dressing and the wound’s needs.
FAQs:
- Q: When should I change a wound dressing?
- A: The frequency of dressing changes depends on the type of dressing and the wound’s needs. Generally, dressings should be changed when they become saturated with exudate, loose, or damaged.
- Q: How do I know if a wound is infected?
- A: Signs of infection include redness, swelling, warmth, pain, pus, and a foul odor. If you suspect an infection, seek medical attention immediately.
Tips:
- Follow a healthcare professional’s instructions for dressing changes and wound care.
- Use sterile gloves and instruments when handling wounds and dressings.
- Observe the wound for any signs of infection and seek medical attention if necessary.
3. Wound Closure Products:
Wound closure products are designed to close wounds and promote healing, reducing the risk of infection and improving aesthetic outcomes. They come in various forms, each suited for specific wound types and closure techniques.
Types of Wound Closure Products:
- Sutures: These are thin, sterile threads used to close wounds by stitching the edges together. They are available in various materials, including nylon, silk, and absorbable materials.
- Staples: These are metal fasteners used to close wounds, particularly those on the scalp or areas where sutures are impractical.
- Adhesive Strips: These are thin, flexible strips that adhere to the skin and hold wound edges together. They are often used for superficial wounds and are particularly suitable for children.
- Tissue Adhesives: These are liquid adhesives that bond wound edges together, creating a seal that promotes healing. They are often used for superficial wounds and can reduce scarring.
- Wound Vacs: These devices use negative pressure to promote wound healing and reduce edema. They are often used for chronic wounds and those with significant tissue loss.
Benefits of Wound Closure Products:
- Improved Healing: Closure products bring wound edges together, promoting proper healing and reducing scarring.
- Reduced Infection Risk: By closing wounds, closure products minimize the risk of bacteria entering the wound and causing infection.
- Faster Healing: Closure products can accelerate the healing process, leading to faster recovery.
- Improved Aesthetics: Closure products can minimize scarring and improve the appearance of wounds.
Considerations:
- Type of Wound: The choice of closure product depends on the wound type, size, location, and patient’s medical history.
- Wound Depth: Deeper wounds may require sutures or staples for proper closure.
- Skin Tension: Closure products should be chosen based on the amount of skin tension present to ensure proper wound closure.
FAQs:
- Q: What are the risks associated with wound closure products?
- A: Potential risks include infection, allergic reactions, and improper wound healing.
- Q: When should I remove stitches or staples?
- A: The removal time varies depending on the wound type and location. A healthcare professional will determine the appropriate time for removal.
Tips:
- Consult a healthcare professional for guidance on wound closure techniques and the appropriate product for specific wounds.
- Follow a healthcare professional’s instructions for wound care and closure product removal.
- Observe the wound for any signs of infection and seek medical attention if necessary.
4. Topical Wound Care Products:
Topical wound care products are applied directly to the wound to promote healing, manage exudate, and prevent infection. They come in various forms, including creams, gels, ointments, and powders.
Types of Topical Wound Care Products:
- Antibiotic Ointments: These ointments contain antibiotics that kill bacteria and prevent infection. They are often used for minor wounds and burns.
- Moisturizing Creams: These creams help keep the wound moist, promoting healing and reducing the risk of scarring.
- Anti-Inflammatory Gels: These gels reduce inflammation and pain, promoting faster healing.
- Wound Healing Powders: These powders absorb excess exudate, keep the wound dry, and promote healing.
- Growth Factors: These products contain proteins that stimulate cell growth and promote wound healing.
Benefits of Topical Wound Care Products:
- Enhanced Healing: Topical products create an optimal environment for wound healing, promoting cell growth and reducing inflammation.
- Infection Prevention: Antibiotic ointments and other antimicrobial agents help prevent infection and protect the wound from bacteria.
- Pain Management: Anti-inflammatory gels and other pain-relieving agents can reduce pain and discomfort.
Considerations:
- Type of Wound: The choice of topical product depends on the wound type, size, and stage of healing.
- Sensitivity: Some topical products can be irritating to sensitive skin, requiring careful selection based on individual tolerance.
- Frequency of Application: The frequency of application depends on the type of product and the wound’s needs.
FAQs:
- Q: Can I use any topical ointment on a wound?
- A: Not all topical ointments are suitable for wounds. Consult a healthcare professional for guidance on the appropriate product for specific wounds.
- Q: How long should I use a topical wound care product?
- A: The duration of use depends on the type of product and the wound’s healing progress. Follow a healthcare professional’s instructions.
Tips:
- Apply topical products according to a healthcare professional’s instructions.
- Wash hands thoroughly before and after applying topical products.
- Observe the wound for any signs of adverse reactions and seek medical attention if necessary.
5. Wound Care Devices:
Wound care devices are tools and instruments used to facilitate wound care, promote healing, and manage complications. They range from simple tools like bandages to complex medical devices used in advanced wound care.
Types of Wound Care Devices:
- Bandages: These are adhesive strips used to cover and protect wounds, providing support and promoting healing. They come in various sizes, shapes, and materials, catering to different wound types and needs.
- Compression Therapy: Compression bandages and garments are used to reduce swelling, improve circulation, and promote healing in wounds like venous ulcers.
- Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT): This advanced technology uses suction to remove exudate, promote wound contraction, and improve blood flow, accelerating healing in complex wounds.
- Pulse Lavage: This technique uses pressurized saline solution to clean wounds and remove debris, effectively preparing them for further treatment.
- Wound Measurement Devices: These devices accurately measure the size and depth of wounds, enabling healthcare professionals to monitor healing progress and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
Benefits of Wound Care Devices:
- Improved Healing: Devices like NPWT and compression therapy promote healing by improving blood flow, removing exudate, and promoting tissue regeneration.
- Infection Control: Devices like bandages and wound irrigation systems help prevent infection by protecting wounds from contaminants.
- Pain Management: Compression therapy and other devices can reduce pain and discomfort associated with wounds.
- Accurate Monitoring: Wound measurement devices provide objective data on wound healing progress, allowing for informed decision-making.
Considerations:
- Type of Wound: The choice of device depends on the wound type, size, location, and patient’s medical history.
- Severity of Wound: Complex wounds may require advanced devices like NPWT or pulse lavage.
- Patient’s Condition: Certain devices may not be suitable for all patients, requiring careful consideration of individual factors.
FAQs:
- Q: How do I use a compression bandage?
- A: Compression bandages should be applied according to a healthcare professional’s instructions to ensure proper fit and effectiveness.
- Q: When is NPWT used?
- A: NPWT is often used for chronic wounds, diabetic ulcers, and wounds with significant tissue loss.
Tips:
- Consult a healthcare professional for guidance on the use of wound care devices and their proper application.
- Follow a healthcare professional’s instructions for device use and maintenance.
- Observe the wound for any signs of complications and seek medical attention if necessary.
Conclusion:
Wound care products play a vital role in promoting healing, preventing infection, and ensuring optimal patient outcomes. Understanding the diverse types of products available, their specific applications, and considerations for their use is crucial for healthcare professionals and individuals managing wounds. By selecting the appropriate products and using them effectively, healthcare practitioners can contribute significantly to the healing process and improve the lives of patients.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Wound Care Products: Types, Applications, and Importance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
