A Comprehensive Guide to Skin Wound Care: Products and Approaches
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Skin Wound Care: Products and Approaches
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Skin Wound Care: Products and Approaches. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Skin Wound Care: Products and Approaches

Skin wounds, ranging from minor abrasions to deep lacerations, are a common occurrence. These injuries disrupt the body’s protective barrier, leaving it vulnerable to infection and compromising its ability to heal. Effective wound care is crucial for promoting rapid recovery, minimizing scarring, and preventing complications. This article delves into the diverse array of products and approaches employed in the treatment of skin wounds, shedding light on their mechanisms of action and highlighting their importance in the healing process.
Understanding Wound Healing: A Complex Process
Wound healing is a multifaceted process that involves a cascade of cellular and molecular events. This intricate choreography aims to restore the integrity of the injured skin, restoring its function and appearance. The process is typically divided into four overlapping stages:
-
Hemostasis: The initial response to injury involves the constriction of blood vessels, followed by the formation of a blood clot to stop bleeding. This clot, composed of platelets and fibrin, forms a provisional matrix that serves as a scaffold for the subsequent stages of healing.
-
Inflammation: The second stage involves the recruitment of inflammatory cells, such as neutrophils and macrophages, to the wound site. These cells clear debris, fight infection, and release growth factors that stimulate tissue repair.
-
Proliferation: This stage is characterized by the formation of new tissue, including fibroblasts that produce collagen, and epithelial cells that migrate across the wound bed to close the gap. New blood vessels also form, providing oxygen and nutrients to the healing tissue.
-
Remodeling: The final stage involves the reorganization and maturation of the newly formed tissue. Collagen fibers are remodeled, leading to increased tensile strength and a reduction in scar tissue.
Product Categories for Wound Care
The products utilized for wound care can be broadly categorized based on their intended function:
1. Wound Cleansing and Debridement:
-
Antiseptics: These agents are used to reduce the number of microorganisms on the wound surface, minimizing the risk of infection. Common antiseptics include:
- Chlorhexidine: A broad-spectrum antiseptic effective against bacteria, fungi, and viruses.
- Povidone-iodine: A potent antimicrobial agent that can be used for both cleansing and debridement.
- Hydrogen peroxide: An oxidizing agent that can be used to cleanse wounds and remove debris.
- Alcohol: Effective against bacteria, but can damage healthy tissue, limiting its use.
- Wound irrigation: Flushing the wound with sterile saline solution or other irrigation solutions helps remove debris, foreign objects, and bacteria, promoting healing.
-
Debridement: This process involves the removal of dead or damaged tissue from the wound bed. It can be performed using various techniques, including:
- Surgical debridement: Performed by a healthcare professional using surgical instruments.
- Sharp debridement: A more controlled method using sharp instruments to remove necrotic tissue.
- Mechanical debridement: Using a gauze or other materials to remove debris.
- Autolytic debridement: Utilizing the body’s natural enzymes to break down dead tissue.
- Enzymatic debridement: Applying commercially available enzymes to dissolve necrotic tissue.
2. Wound Protection and Moisture Management:
-
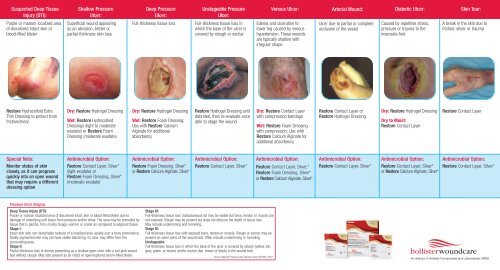
Wound dressings: These materials are designed to protect the wound from external contamination, absorb exudate, and maintain a moist healing environment. Different types of dressings cater to specific wound characteristics:
- Gauze dressings: Versatile and inexpensive, but can adhere to the wound bed.
- Hydrocolloid dressings: Form a gel-like barrier that absorbs exudate and provides a moist environment.
- Hydrogel dressings: Hydrating dressings that can help rehydrate the wound bed.
- Foam dressings: Highly absorbent dressings that are ideal for wounds with moderate to heavy exudate.
- Alginate dressings: Absorbent dressings made from seaweed that are particularly effective for wounds with heavy exudate.
- Transparent film dressings: Allow for visualization of the wound while providing a barrier against bacteria.
- Antimicrobial dressings: These dressings incorporate antimicrobial agents to prevent infection.
3. Wound Healing Enhancement:
- Growth factors: These proteins stimulate the growth and proliferation of cells involved in wound healing.
- Collagen-based products: These products provide a scaffold for new tissue growth and promote collagen synthesis.
- Skin grafts: In cases of extensive tissue loss, skin grafts can be used to replace damaged skin.
- Negative pressure wound therapy: This technique applies negative pressure to the wound bed, promoting drainage, reducing edema, and stimulating tissue regeneration.
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy: This treatment involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber, increasing the oxygen levels in the wound and promoting healing.
4. Pain Management:
- Topical analgesics: These medications can be applied directly to the wound to reduce pain.
- Oral analgesics: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or other pain relievers may be prescribed to manage pain.
Importance of Effective Wound Care
Effective wound care is paramount for optimal healing and minimizing complications. It plays a crucial role in:
- Preventing infection: Proper wound cleansing and protection reduce the risk of bacterial contamination, minimizing the likelihood of infection.
- Promoting tissue regeneration: Creating a moist, optimal environment for wound healing facilitates the growth of new tissue and promotes rapid healing.
- Minimizing scarring: By ensuring proper wound closure and promoting tissue regeneration, effective wound care can minimize the formation of unsightly scars.
- Reducing pain and discomfort: Pain management strategies alleviate pain and discomfort, improving the patient’s quality of life during the healing process.
FAQs Regarding Wound Care Products
Q: What are some common signs of wound infection?
A: Signs of wound infection include redness, swelling, warmth, pain, pus, and foul odor. If you notice any of these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
Q: How often should I change my wound dressing?
A: The frequency of dressing changes depends on the type of wound, the amount of exudate, and the type of dressing used. Consult with a healthcare professional for specific guidance.
Q: Can I use over-the-counter wound care products for all types of wounds?
A: Over-the-counter products are generally safe for minor wounds, but for more serious injuries, it is crucial to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can assess the wound and recommend appropriate products and treatments.
Q: How long does it take for a wound to heal?
A: The healing time varies depending on the size, depth, and location of the wound, as well as the individual’s health status. Minor wounds may heal within a few days, while more severe wounds may take several weeks or months.
Q: What should I do if a wound is not healing properly?
A: If a wound is not showing signs of improvement or is becoming worse, seek medical attention immediately. This could indicate an infection or other complications that require specialized treatment.
Tips for Effective Wound Care
- Keep the wound clean: Gently cleanse the wound with sterile saline solution or an antiseptic as directed by a healthcare professional.
- Apply a wound dressing: Choose a dressing appropriate for the type of wound and follow instructions for application and changing.
- Protect the wound from contamination: Avoid touching the wound with bare hands and keep it covered with a dressing.
- Monitor the wound for signs of infection: Observe for redness, swelling, warmth, pain, pus, or foul odor. Seek medical attention if any of these symptoms develop.
- Promote wound healing: Follow a healthy diet, get enough rest, and avoid smoking to promote optimal wound healing.
Conclusion
Effective wound care is essential for promoting rapid healing, minimizing scarring, and preventing complications. Understanding the different stages of wound healing and the various products and approaches available is crucial for providing optimal care. By following these guidelines and seeking professional guidance when necessary, individuals can ensure proper wound management and facilitate optimal healing outcomes. Remember, prompt and appropriate wound care is key to restoring the integrity of the skin and promoting overall well-being.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Skin Wound Care: Products and Approaches. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
