A Comprehensive Guide to Skin Viruses: Understanding the Invisible Invaders
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Skin Viruses: Understanding the Invisible Invaders
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Skin Viruses: Understanding the Invisible Invaders. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Skin Viruses: Understanding the Invisible Invaders

The skin, our body’s largest organ, serves as a crucial barrier against the external environment. While this protective shield is formidable, it is not impervious. Viruses, microscopic entities capable of replicating within living cells, can breach this barrier, leading to a range of skin conditions. Understanding these viral infections is vital for effective prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.
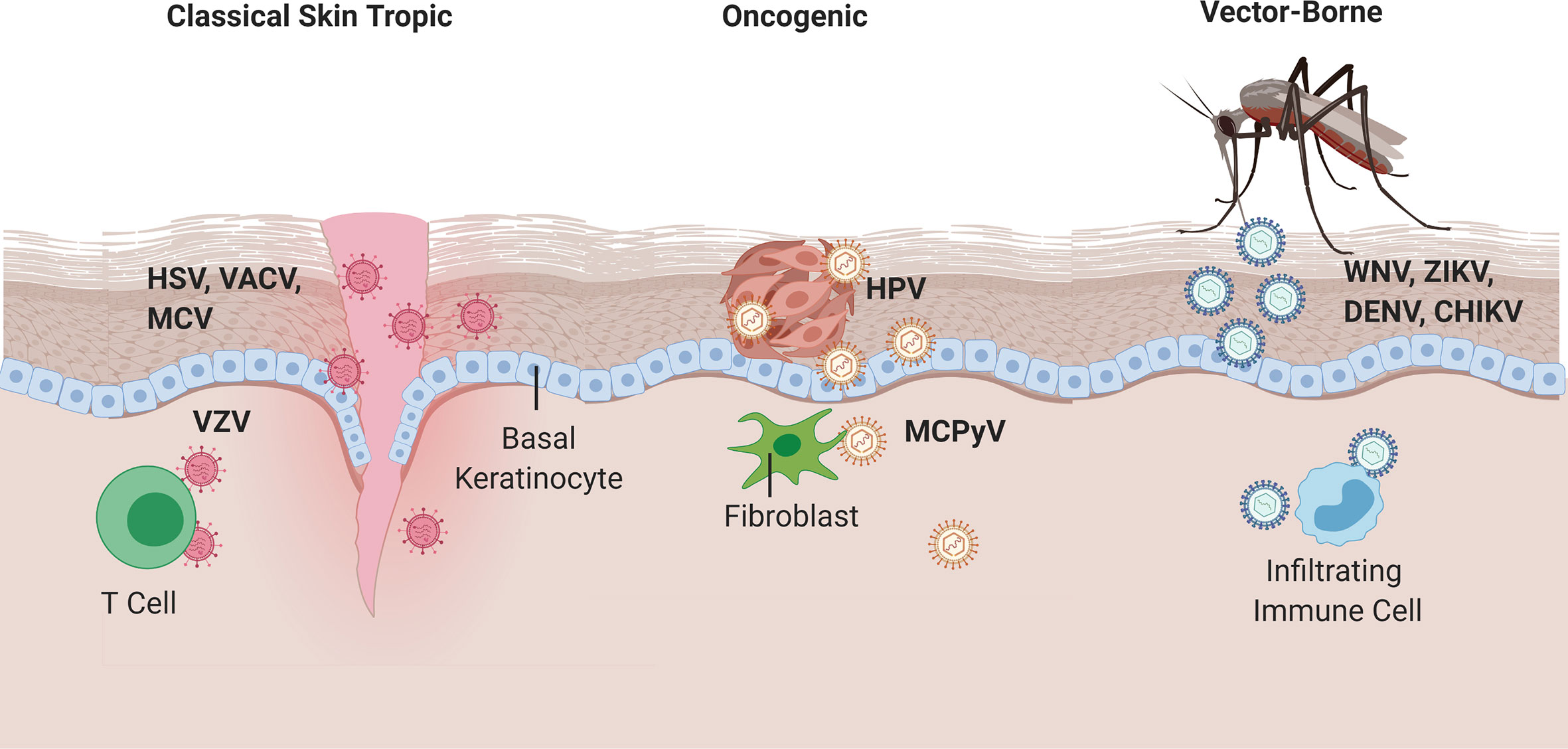
Viral Infections Affecting the Skin: A Diverse Landscape
Viruses that target the skin exhibit a diverse range of characteristics, leading to distinct clinical presentations and varying levels of severity. Here’s a breakdown of some of the most common viral skin infections:
1. Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) Infections:
- Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 (HSV-1): Primarily responsible for oral herpes, commonly known as cold sores or fever blisters. These lesions typically appear around the mouth, lips, and face.
- Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 (HSV-2): Primarily responsible for genital herpes, causing painful blisters and sores in the genital area.
Characteristics:
- Transmission: HSV is spread through direct contact with infected lesions, saliva, or bodily fluids.
- Clinical Presentation: HSV infections manifest as characteristic fluid-filled blisters that eventually rupture, leaving behind sores that crust over and heal.
- Recurrence: HSV can lie dormant in nerve cells and reactivate, causing recurrent outbreaks triggered by stress, illness, or sunlight exposure.
2. Varicella-Zoster Virus (VZV):
- Chickenpox (Varicella): A highly contagious childhood disease characterized by itchy, fluid-filled blisters that appear all over the body.
- Shingles (Herpes Zoster): A reactivation of the VZV virus that lies dormant after chickenpox infection. Shingles causes painful, blistering rashes that typically affect one side of the body.
Characteristics:
- Transmission: VZV is spread through direct contact with infected lesions or respiratory droplets.
- Clinical Presentation: Chickenpox presents with a characteristic itchy rash, while shingles causes a painful, localized rash often accompanied by fever and chills.
- Immunization: Vaccination is available for both chickenpox and shingles, significantly reducing the risk of infection and complications.
3. Human Papillomavirus (HPV):
- Warts: HPV is a group of viruses that cause various types of warts on the skin. Common warts are found on the hands and fingers, while plantar warts appear on the soles of the feet. Genital warts are sexually transmitted and can lead to cervical cancer.
Characteristics:
- Transmission: HPV is spread through direct contact with infected skin or mucous membranes.
- Clinical Presentation: Warts appear as small, raised growths that can be flesh-colored, gray, or brown.
- Treatment: Warts can be treated with topical medications, cryotherapy, or laser therapy.
4. Molluscum Contagiosum Virus (MCV):
- Molluscum Contagiosum: A skin infection characterized by small, pearly, dome-shaped bumps that can appear anywhere on the body.
Characteristics:
- Transmission: MCV is spread through direct contact with infected skin or through contaminated objects.
- Clinical Presentation: Molluscum lesions are typically painless and can range in size from a pinhead to a pea.
- Treatment: Molluscum lesions can be treated with topical medications, freezing, or laser therapy.
5. Parvovirus B19:
- Fifth Disease (Erythema Infectiosum): A common childhood illness characterized by a distinctive "slapped cheek" rash on the face.
Characteristics:
- Transmission: Parvovirus B19 is spread through respiratory droplets.
- Clinical Presentation: Fifth disease begins with fever, headache, and runny nose, followed by a characteristic bright red rash on the cheeks.
- Complications: In rare cases, parvovirus B19 can cause complications in pregnant women or people with weakened immune systems.
Understanding the Importance of Skin Virus Awareness
Recognizing the diverse nature of skin viruses is crucial for effective management and prevention. Knowledge empowers individuals to:
- Seek Prompt Medical Attention: Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and reduce the risk of spreading the virus.
- Practice Effective Prevention: Understanding the modes of transmission allows for informed decisions regarding hygiene, contact precautions, and vaccination.
- Promote Public Health: Awareness of skin viruses can help to prevent outbreaks and protect vulnerable populations.
FAQs Regarding Skin Viruses
1. Are all skin viruses contagious?
Yes, most skin viruses are contagious and can be spread through direct contact, contaminated objects, or respiratory droplets.
2. Can skin viruses be prevented?
While not all skin viruses can be completely prevented, several measures can significantly reduce the risk of infection, including:
- Good hygiene: Regular handwashing, covering coughs and sneezes, and avoiding contact with infected lesions can help prevent the spread of viruses.
- Vaccination: Vaccines are available for chickenpox, shingles, and HPV, offering significant protection against these viruses.
- Safe sex practices: Using condoms during sexual activity can help prevent the transmission of sexually transmitted viruses like HSV-2 and HPV.
3. How are skin viruses treated?
Treatment for skin viruses varies depending on the specific virus and the severity of the infection. Some common treatment approaches include:
- Antiviral medications: Antiviral drugs can help to suppress the virus and reduce the duration and severity of symptoms.
- Topical treatments: Creams, lotions, or ointments can be applied to the affected area to relieve symptoms and promote healing.
- Immunotherapy: In some cases, immunotherapy may be used to boost the body’s immune response to the virus.
4. Can skin viruses cause long-term health problems?
While most skin viruses resolve on their own, some can lead to long-term complications, such as:
- Herpes Simplex Virus: Recurrent outbreaks, corneal ulcers, and encephalitis.
- Varicella-Zoster Virus: Postherpetic neuralgia, a chronic pain condition that can persist after shingles.
- Human Papillomavirus: Genital warts, cervical cancer, and other cancers.
5. What can I do if I think I have a skin virus?
If you suspect you may have a skin virus, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment. They can determine the specific virus responsible for your symptoms and recommend the appropriate course of action.
Tips for Preventing Skin Virus Infections
- Maintain good hygiene: Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially after touching infected lesions or contaminated surfaces.
- Avoid close contact with infected individuals: Stay away from people who have active skin infections.
- Keep wounds clean and covered: Clean and cover any cuts or wounds to prevent infection.
- Practice safe sex: Use condoms to reduce the risk of sexually transmitted viruses.
- Get vaccinated: Vaccines are available for chickenpox, shingles, and HPV, offering significant protection against these viruses.
Conclusion
Understanding the diverse landscape of skin viruses is essential for maintaining skin health and preventing the spread of infection. By staying informed about these invisible invaders, practicing preventive measures, and seeking prompt medical attention when necessary, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing skin virus infections and their potential complications. Continued research and advancements in antiviral therapies offer hope for even more effective prevention and treatment options in the future.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Skin Viruses: Understanding the Invisible Invaders. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
